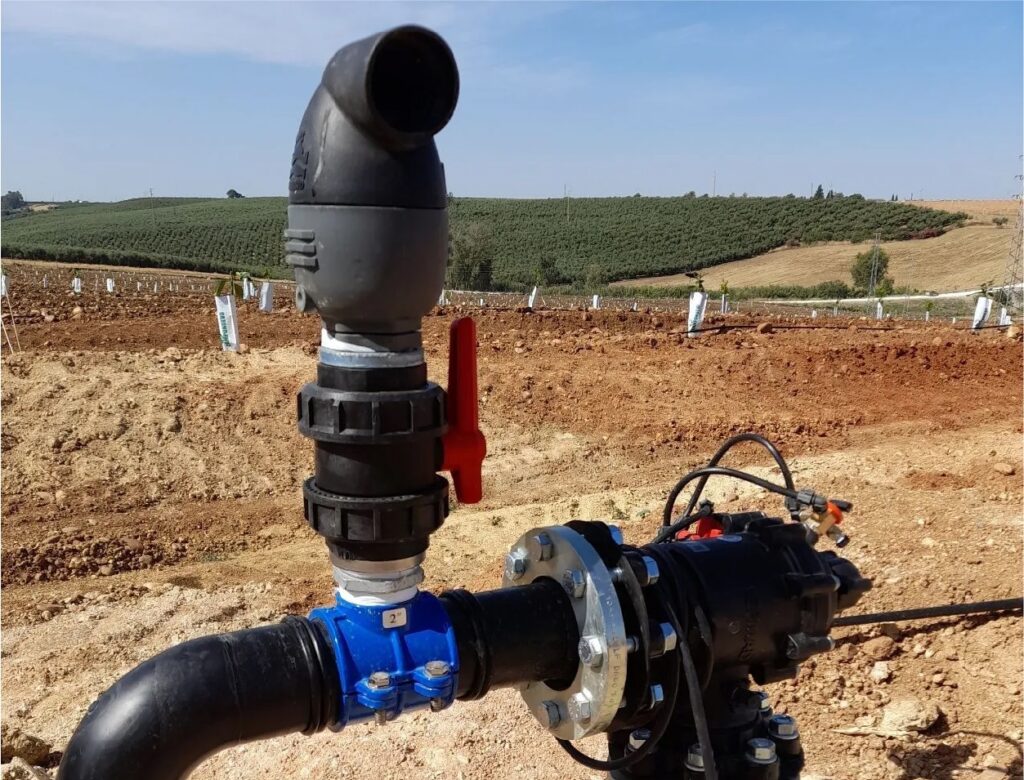
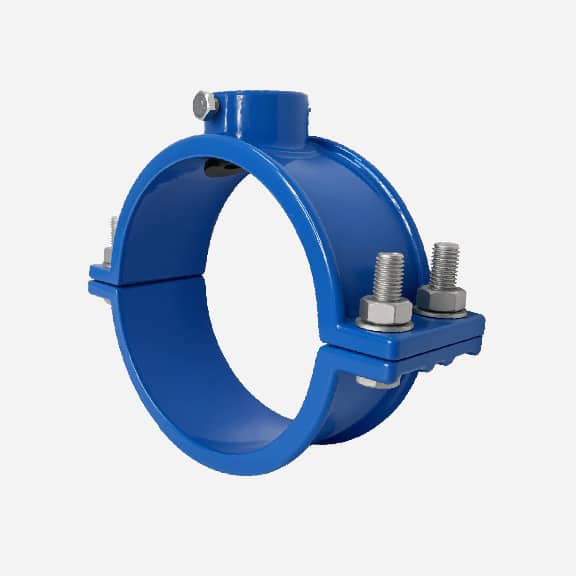
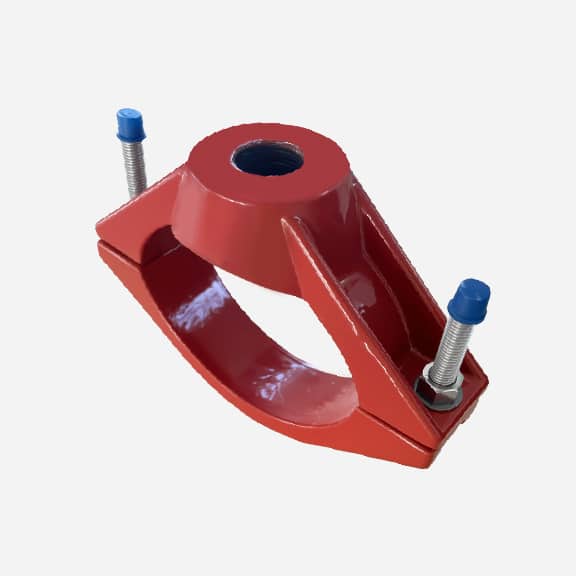
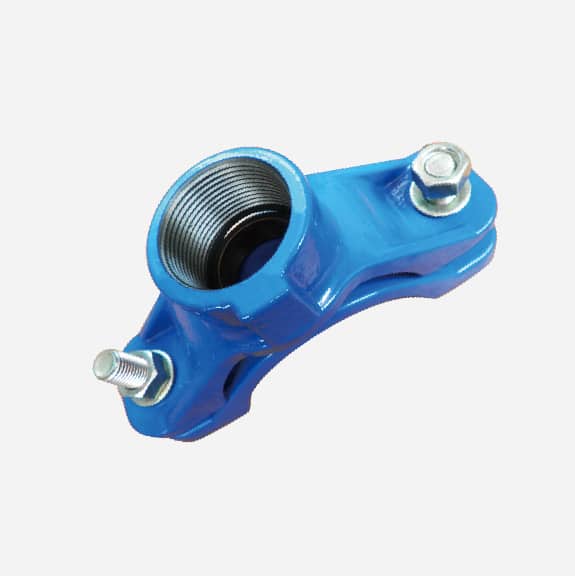
SADDLE CLAMP MANUFACTURER
A saddle clamp is a device used to tap into a main pipeline. It wraps around the pipe and diverts flow out of the main pipe.
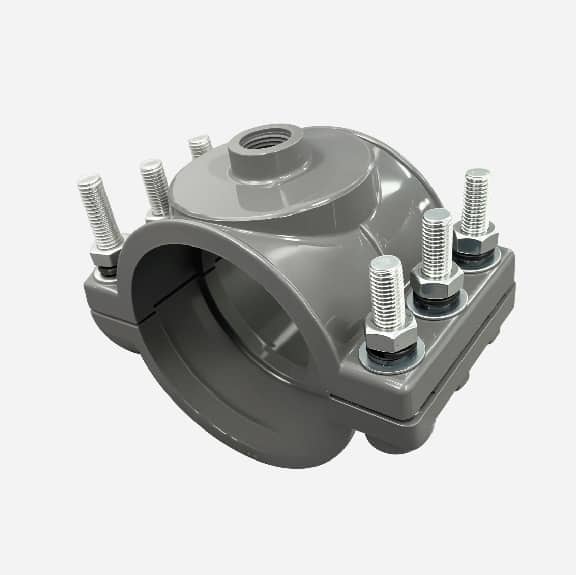
Typically, the two pieces of the saddle clamp are squeezed together with tightening bolts to secure it tightly to the pipe. A sealing gasket is compressed between the saddle clamp and the pipe to ensure a tight seal and no leaks at the tapping point.
Judberd produce castings on auto production line, so we have much more competitive price, very good quality and fast delivery time.
In addition, we can also customize the saddle clamp to meet client specific needs.
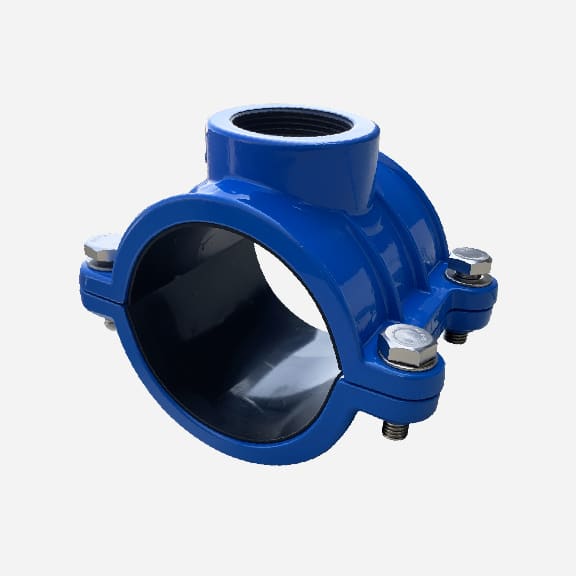
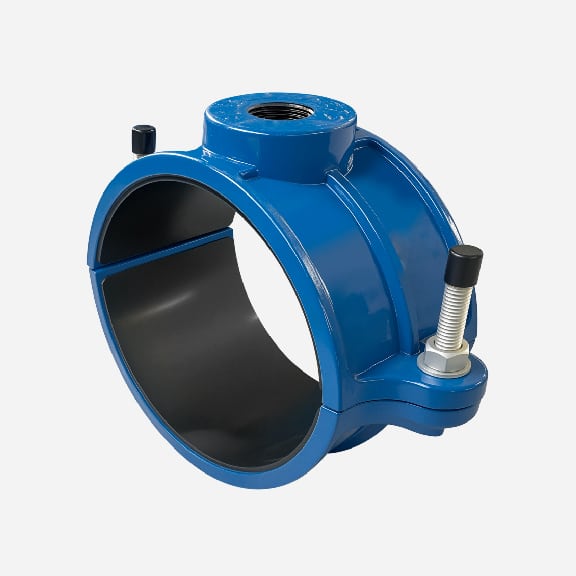
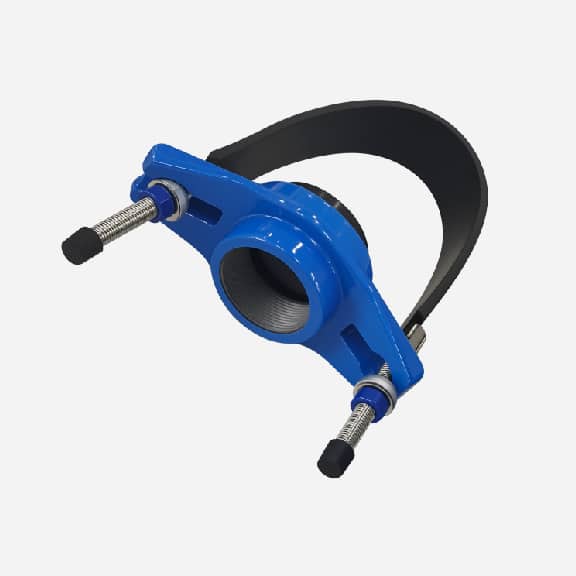
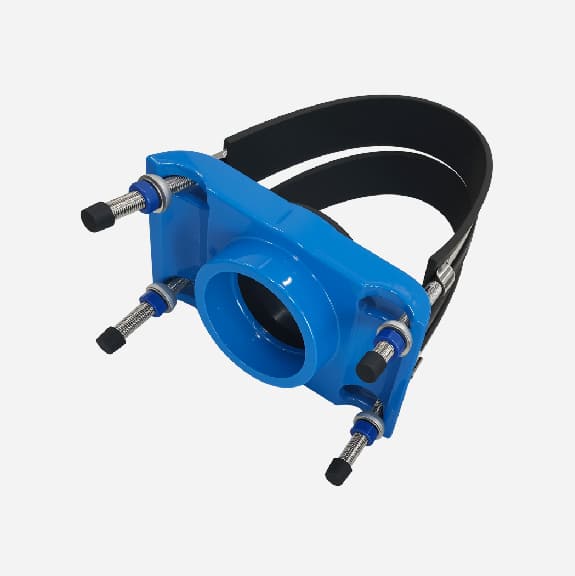
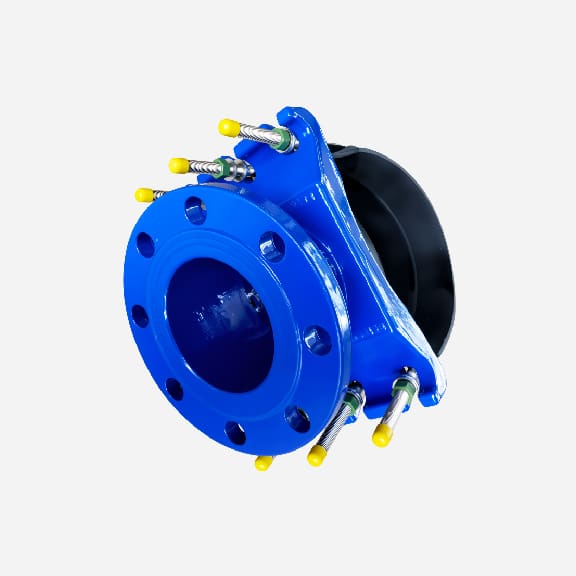
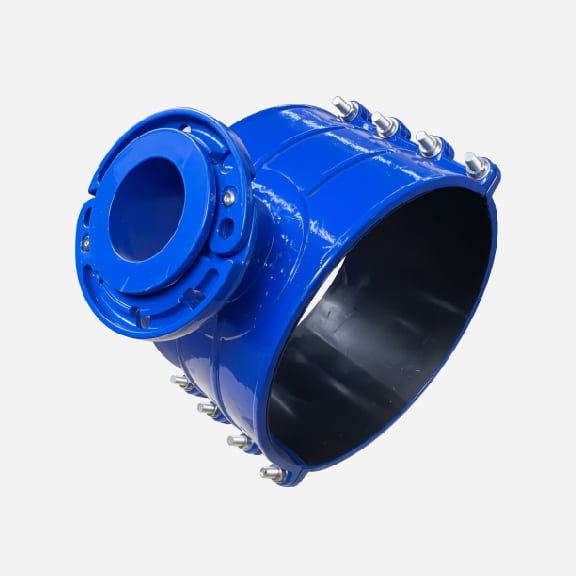
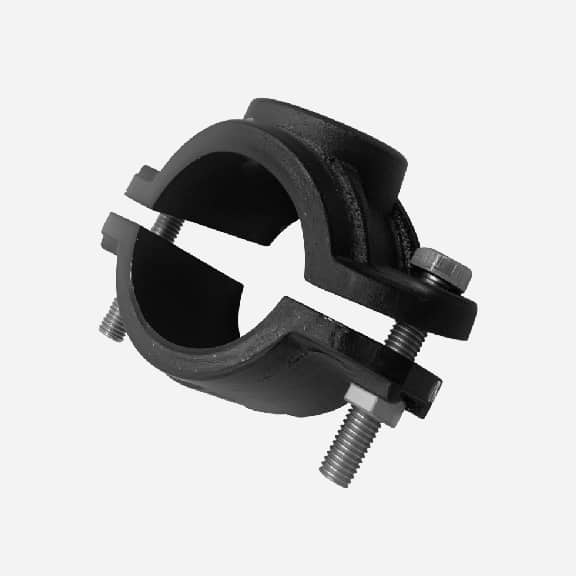
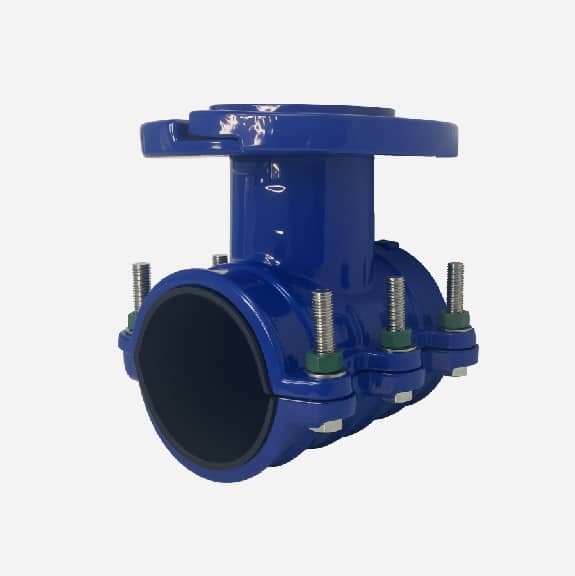
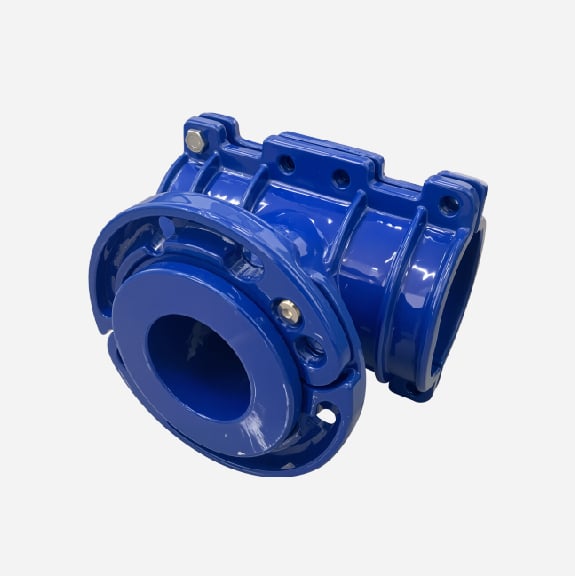
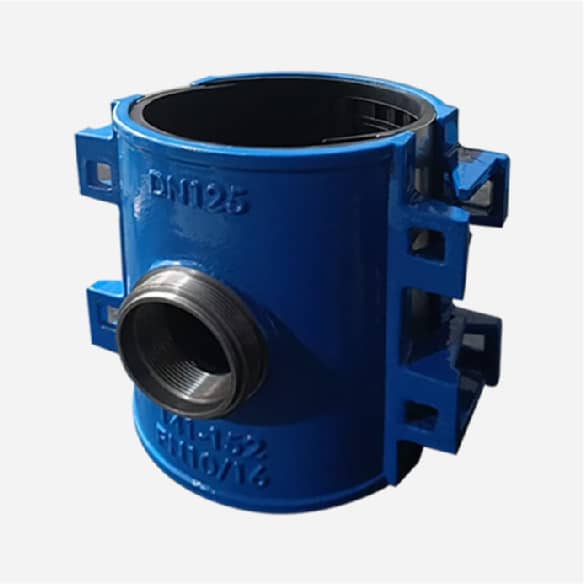
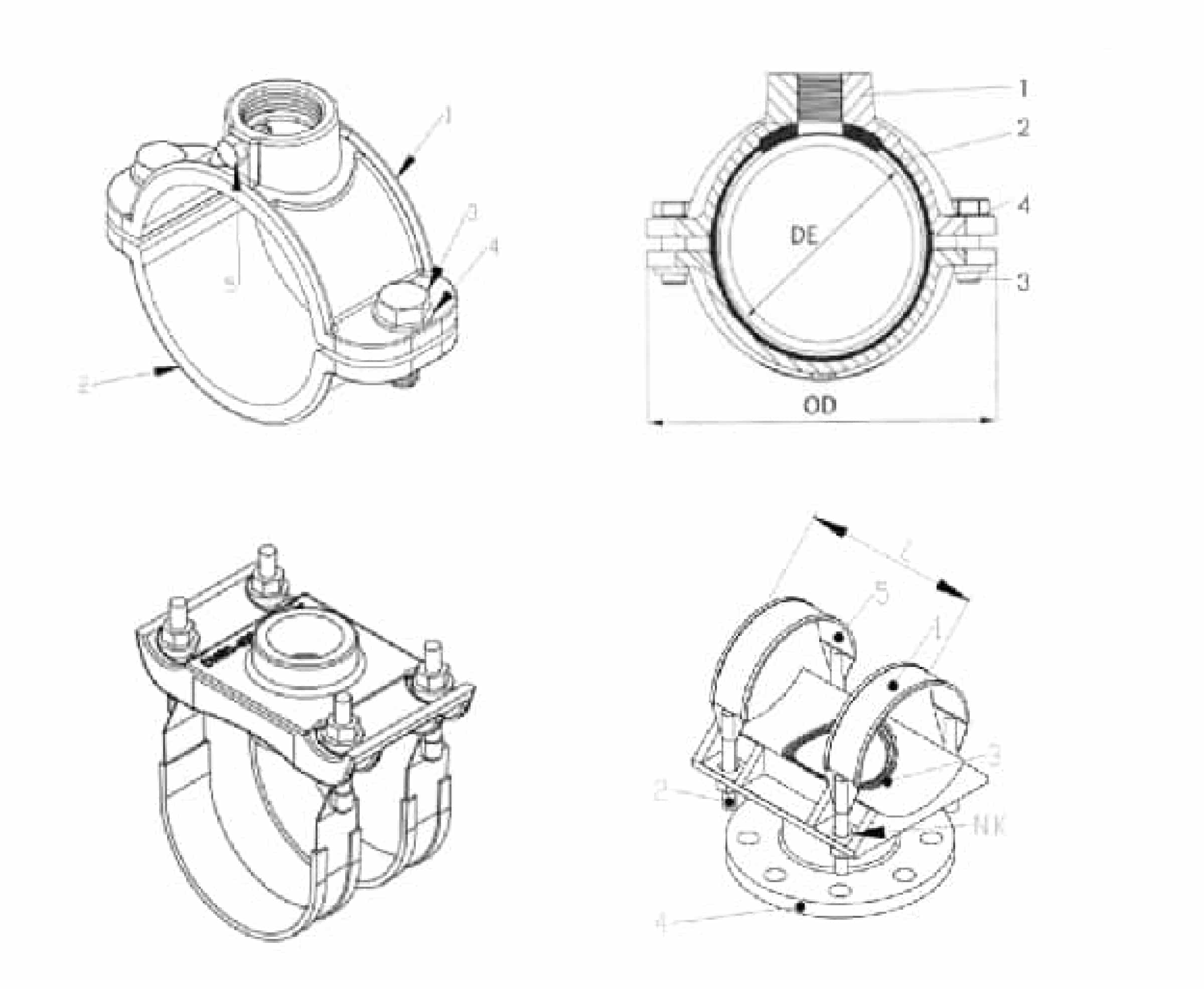
Wide range saddle clamp for ductile iron pipe, steel pipe, GRP pipe etc,not suitable for HDPE and PVC pipe
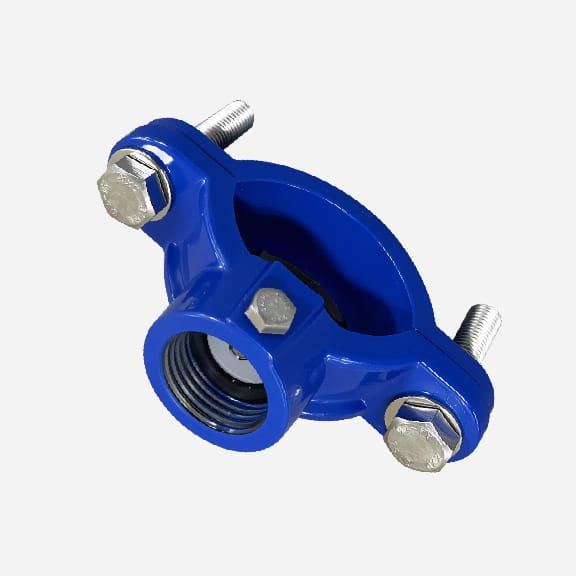
Universal Saddle tap for Ductile Iron Pipe,PVC pipe,Steel Pipe ,PE Pipe etc, thread outlet ,single steel strip
Universal saddle for ductile iron pipe, pvc pipe, steel pipe etc, thread outlet, double steel strips
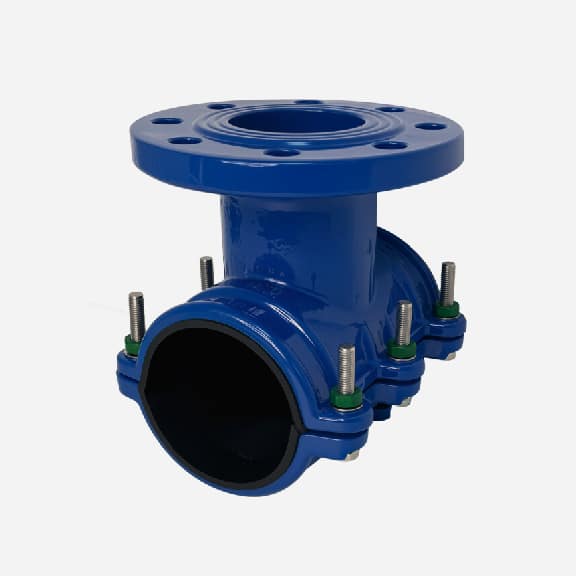
Universal saddle for ductile iron pipe, pvc pipe, steel pipe etc, flange outlet, multiple steel strips
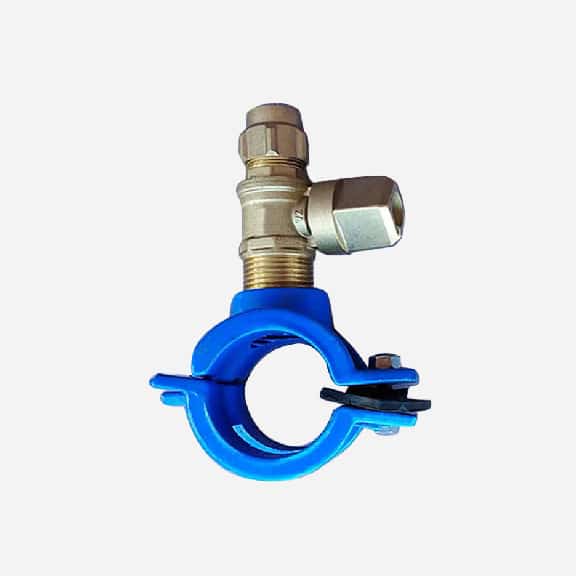
Repair saddle clamp, can work as repair clamp without thread outlet, also can work as saddle clamp with thread outlet
VIDEO
WHY JUDBERD SADDLE CLAMP?
Various design to meet the different needs of our customers.
We have professional research and design department that can design according to the requirements of our customers.
Our saddle clamps not only work well, they also have a long service life, are easy to install and are people friendly.
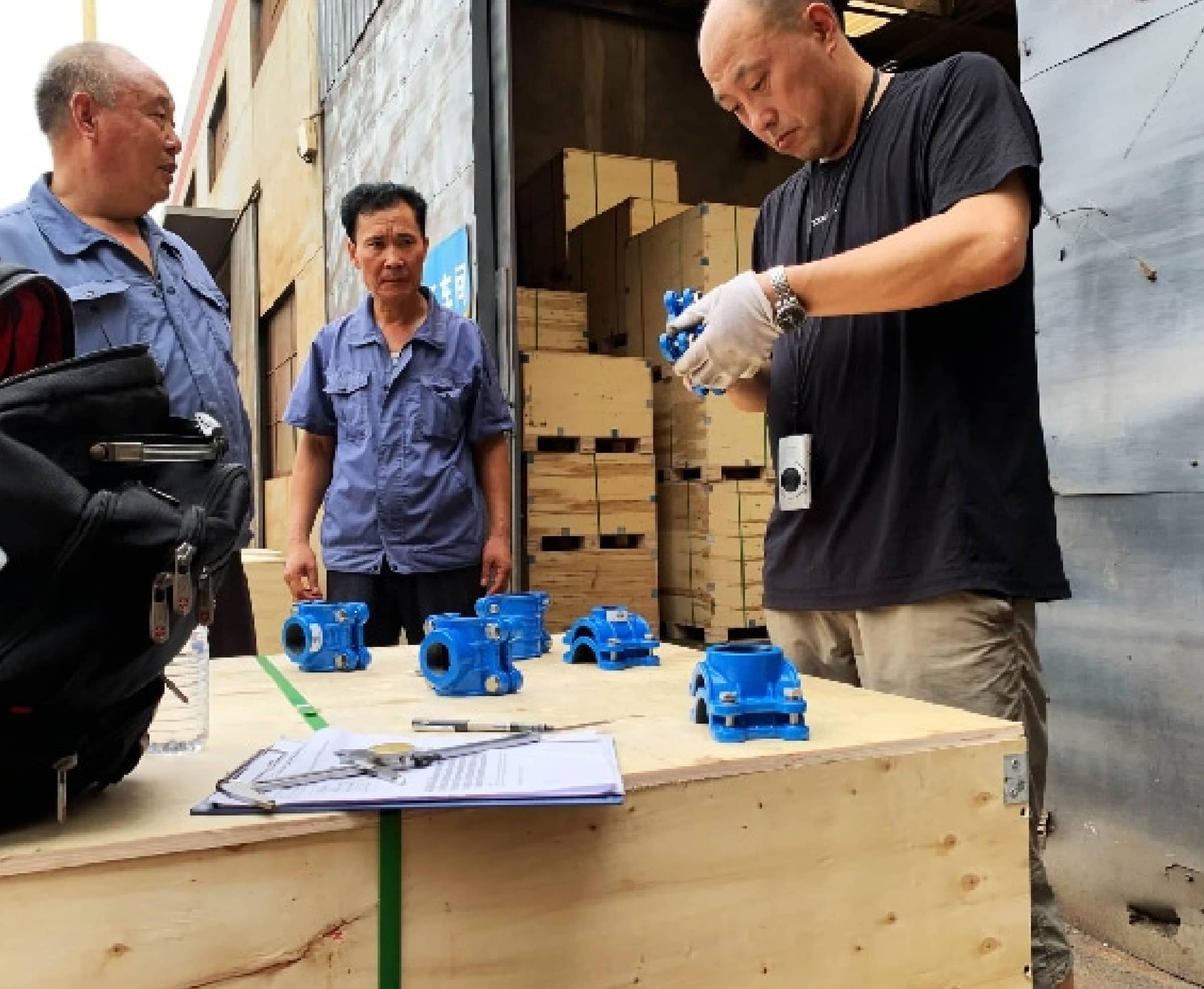

Factory self-inspection, customer inspection or third-party inspection are very welcome, and can issue 3.1 inspection certificate or other inspection certificates according to customer requirements.
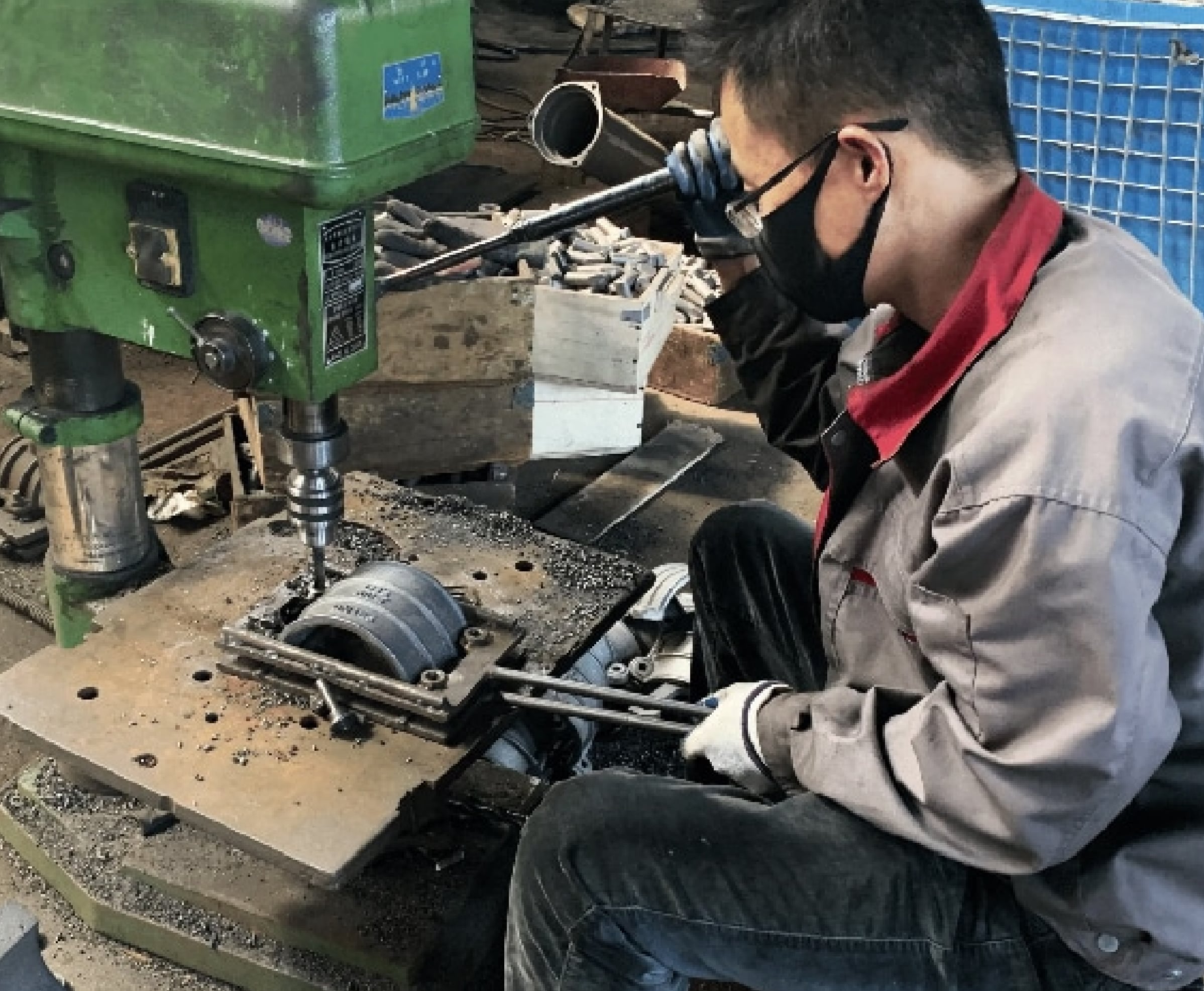

Judberd is a saddle manufacturer with more than 30 years of production experience, supplying many well-known brands.
We are familiar with every production process of saddle so that we can provide products with good quality and low price.
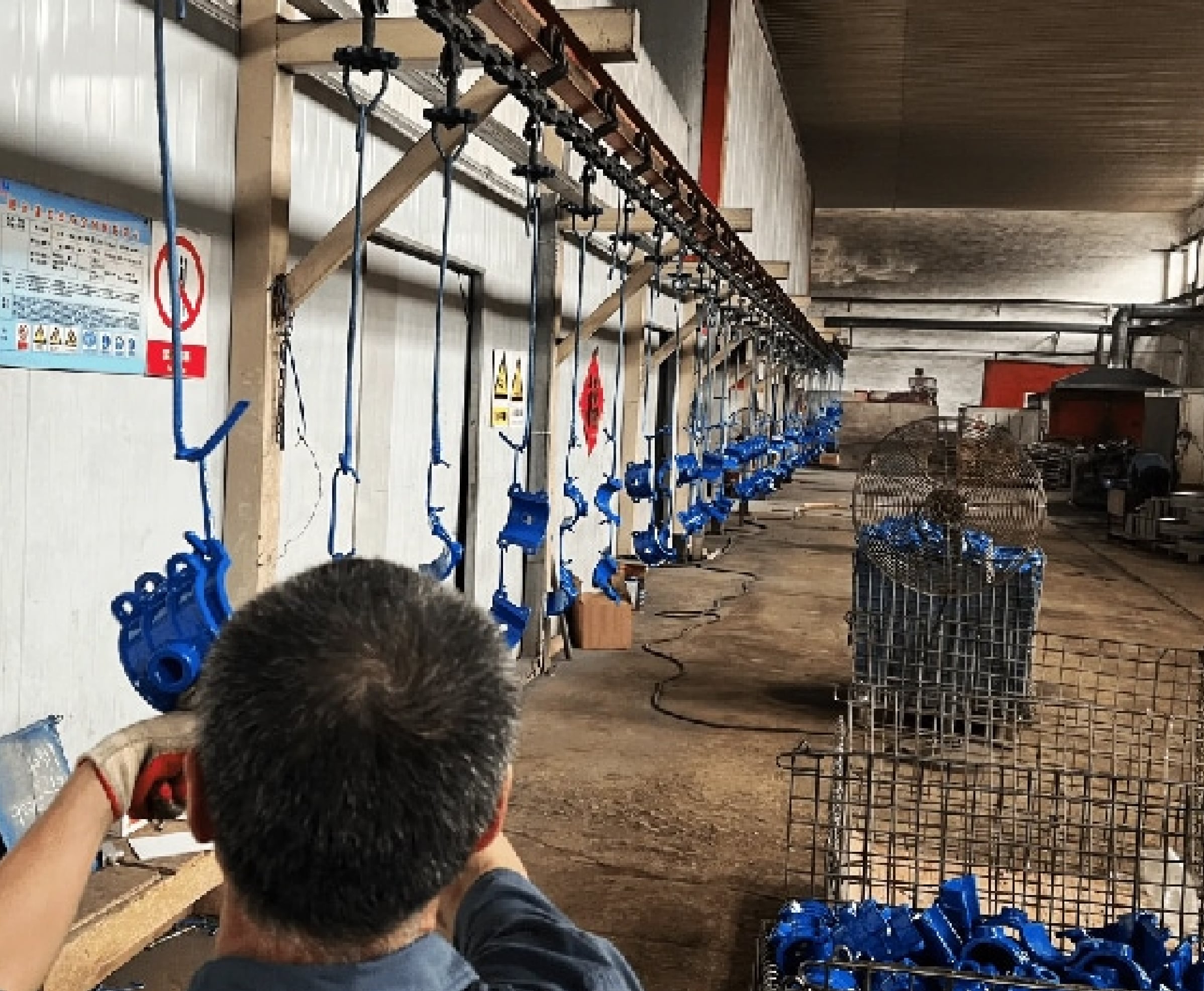

The surface of the saddle clamp can be FBE Coating, nylon11 coating or other coatings required by the customer.

We have improved our process and now produce castings on a vertical automatic production line, the quality of our saddle clamp is better than before and the price is cheaper.
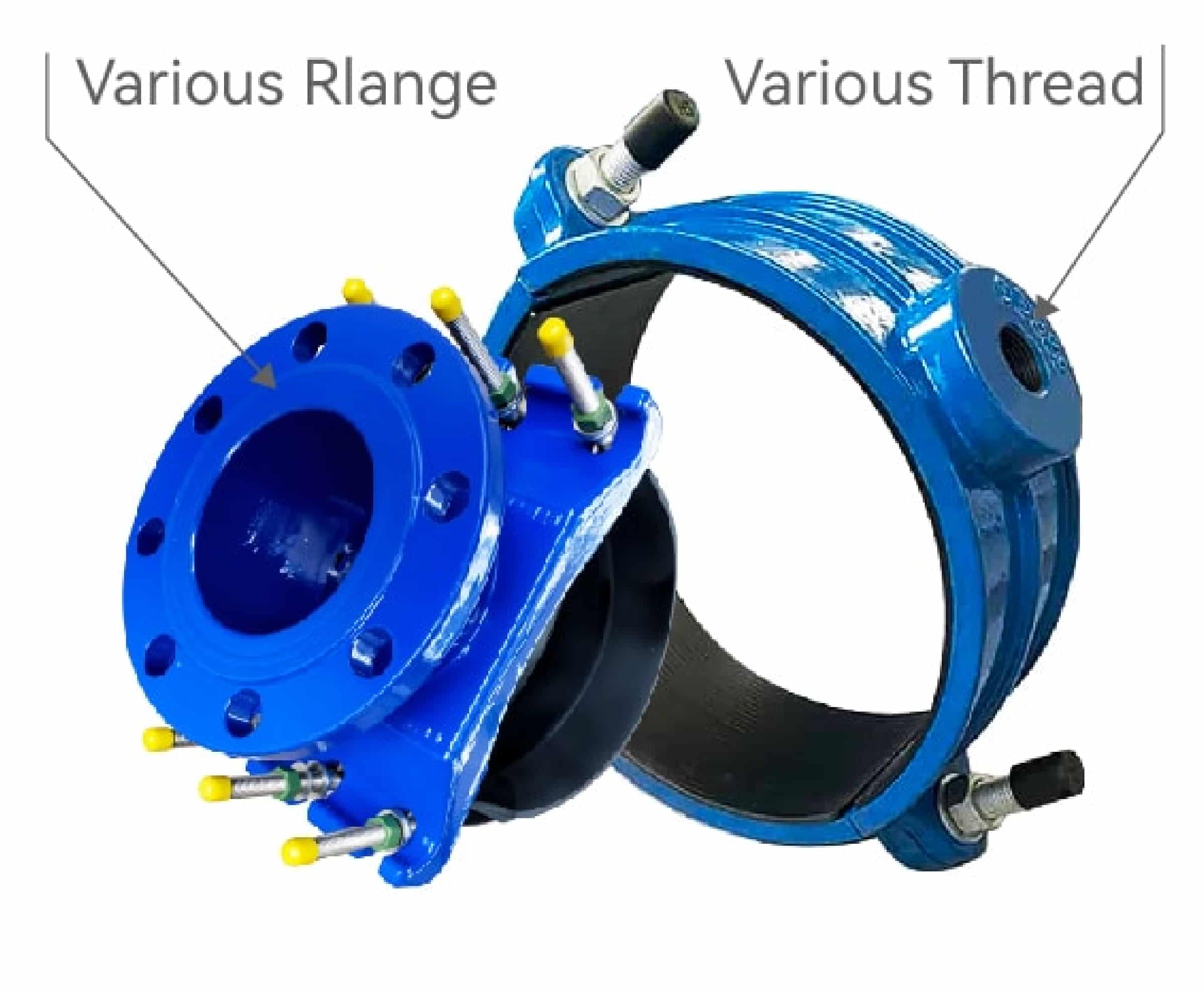

We can provide saddle clamp with BSP thread, NPT thread, CC thread, Metric thread etc threaded outlet, or EN1092-2, ANSI B16.5/ANSI B 16.47, AS4087 etc standard flange.

Bolts can be dacromet, galvanized, geomet, teflon coated grade 4.8, 6.8 or 8.8 carbon steel , or stainless steel SS304/SS316 etc.
HOW TO PRODUCE SADDLE CLAMP?

Casting by automatic moulding line

Polishing

Drilling the bolts holes

Coating
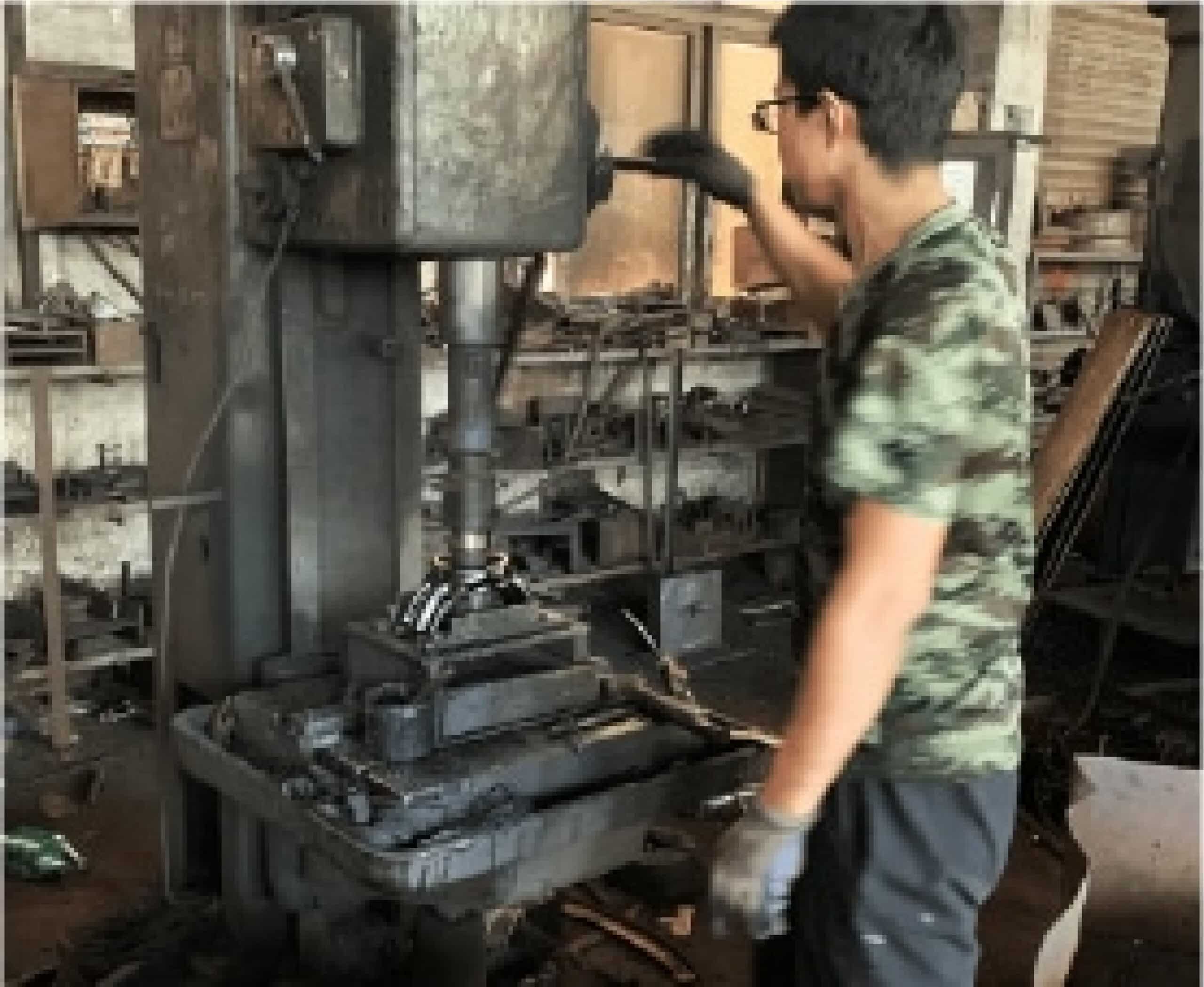

Drilling outlet thread and bolts thread
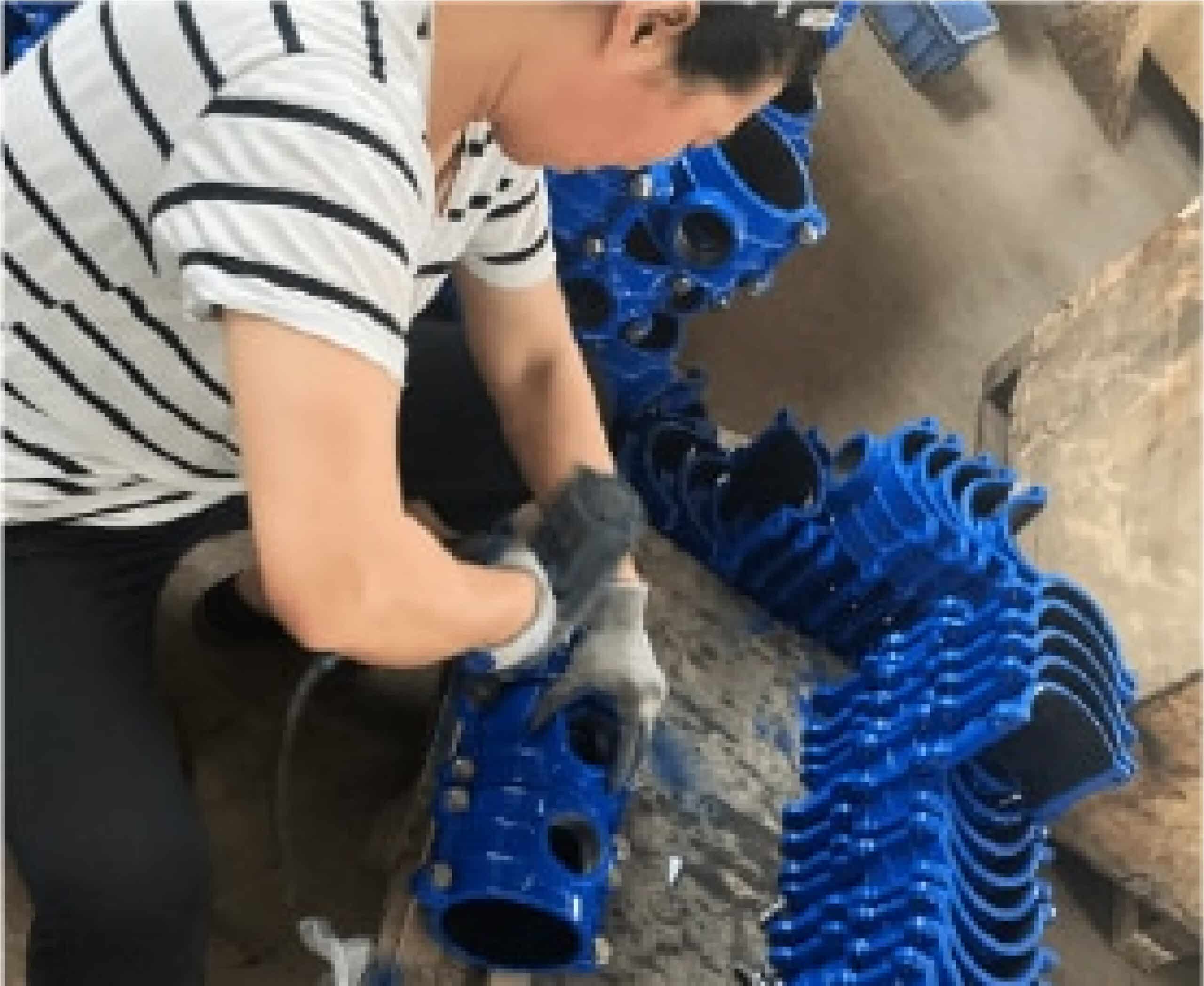

Assembling
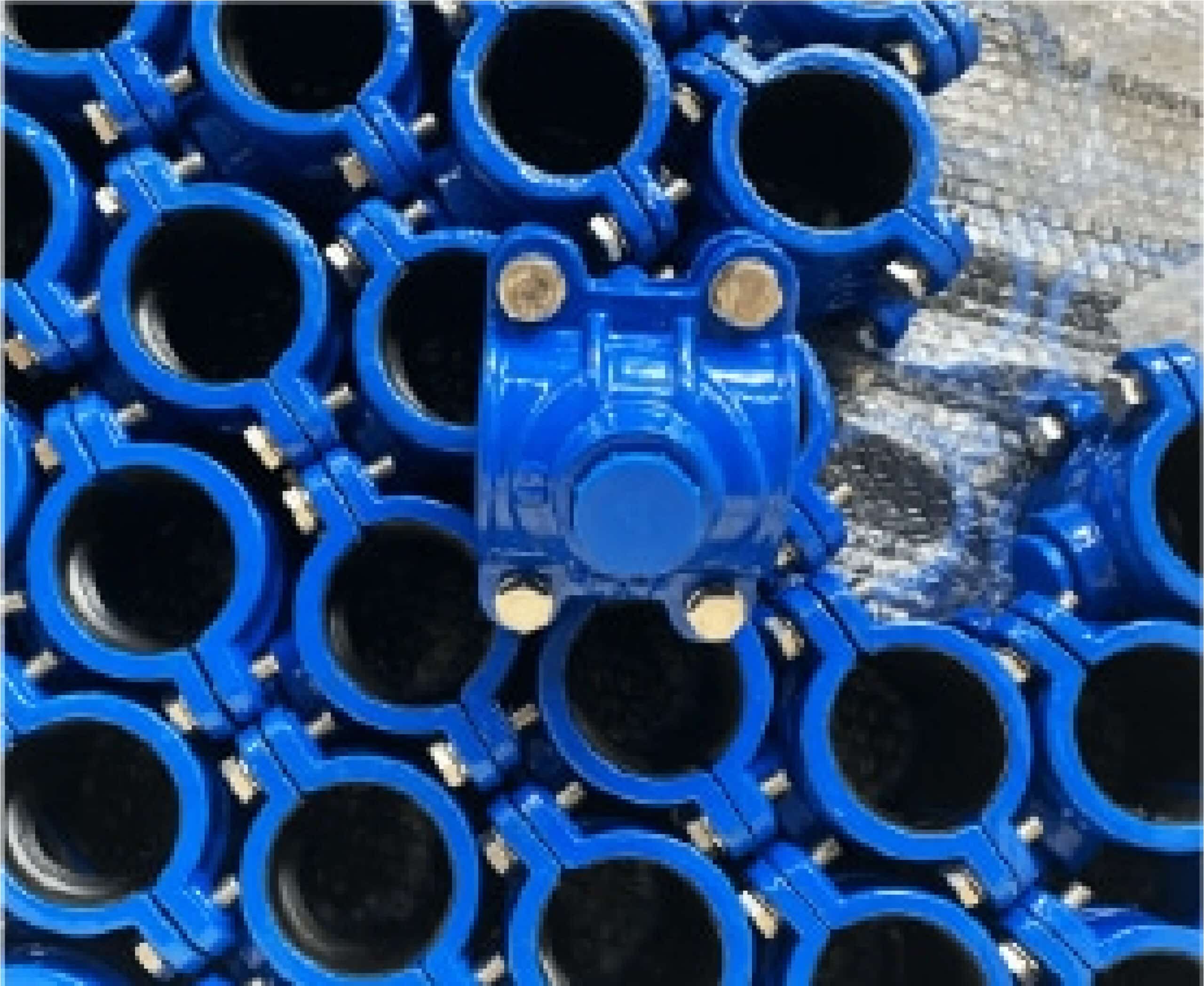

Package
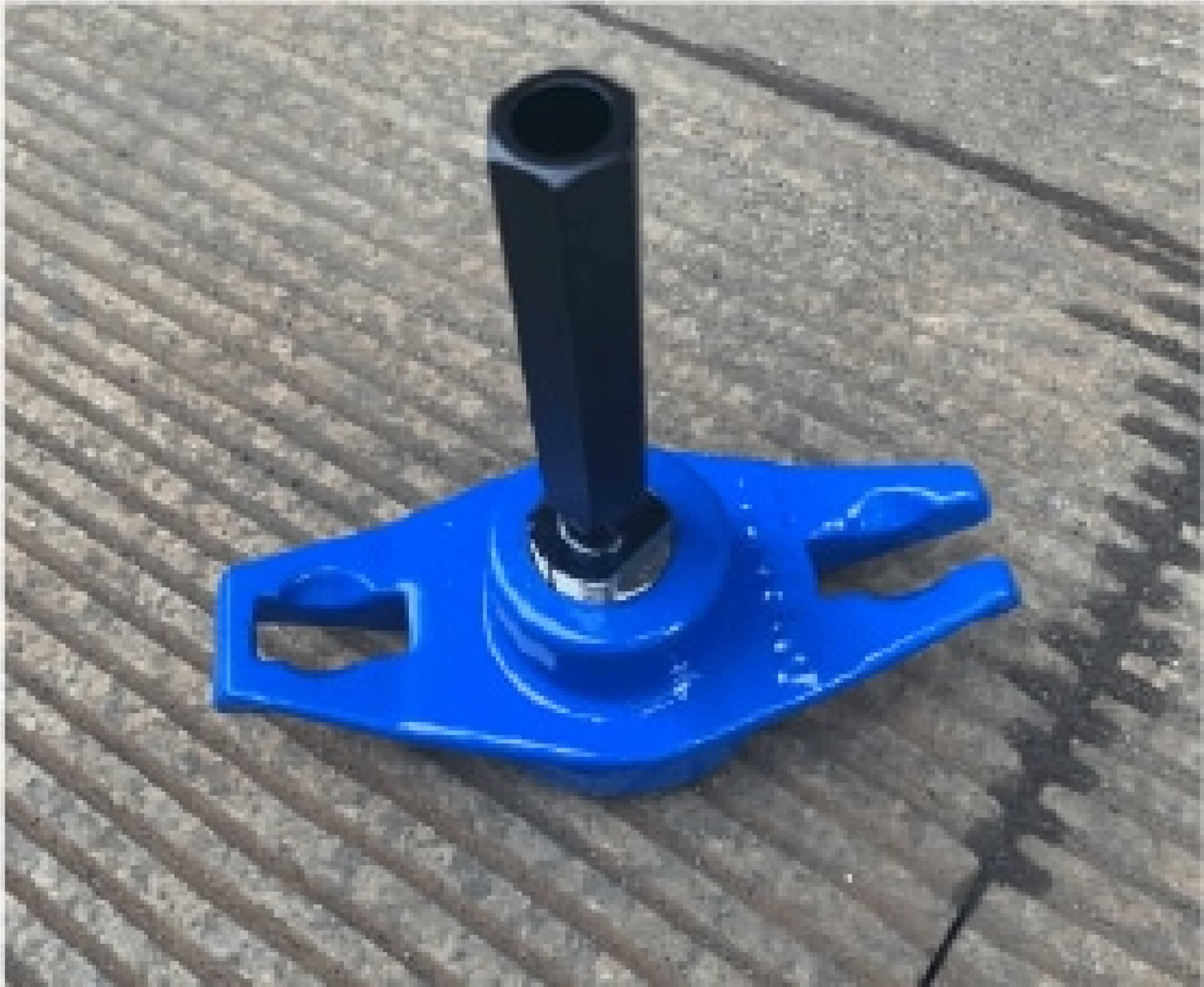

Inspection after each production step
SADDLE CLAMPS DIMENSION
If you want to buy the right saddle clamp, you need to confirm the following dimensions with the manufacturer.
The material of the main pipe
If the material of the main pipe is hard (such as steel pipe, iron pipe), the saddle clamp needs more clamping force and more precise dimensions to ensure reliable installation and sealing. So you can choose a narrower saddle clamp.
If the material of the main pipe is soft (such as plastic pipe PE pipe, PVC pipe, etc.), the design of the saddle clamp may need to consider a larger clamping area to distribute pressure, avoid pipe deformation or damage. Therefore, a wider saddle clamp is needed.
The outside diameter of the main pipe (Pipe Outside Diameter)
This is the most important dimension, which refers to the outside diameter of the main pipe that the saddle clamp needs to branch. It must be precise to ensure that the saddle clamp can be correctly installed on the pipe.
Branch size and branch type (threaded connection, flange connection, welding, etc.)
This refers to the diameter of the branch pipe that branches out from the saddle clamp. This size determines the size of the branch pipe. The branch pipe is commonly threaded and flanged. Threaded outlets are typically used for smaller outlets, generally up to 3 inches in size.Threaded connections include sealing threaded connections (BSP thread, NPT thread, CC thread, etc.) and non-sealing threaded connections (Metric thread). If it is a sealing threaded connection, you can seal the saddle clamp and the isolation valve through the thread. If it is a non-sealing threaded connection, the end of the isolation valve and the gasket need to be squeezed to form a seal.
Providing these dimensions to the manufacturer will ensure that you get the right saddle clamp to suit your specific application needs.
SADDLE CLAMPS DRAWING
Judberd can design saddle clamp according to customer requirements, As long as customers provide specific requirements, we can offer professionally functional saddle clamp. Below are the drawings we have designed for our customers, for your reference.
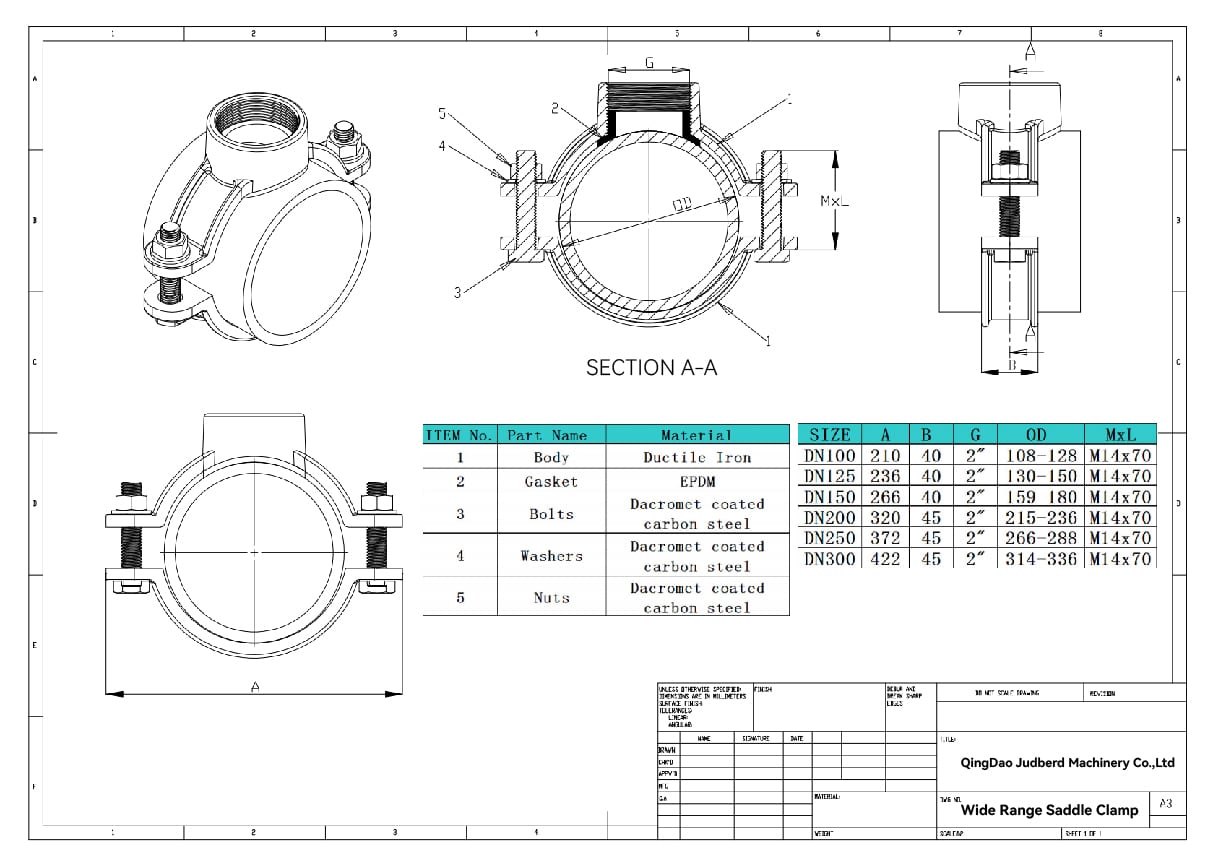
WIDE RANGE SADDLE CLAMP DRAWING
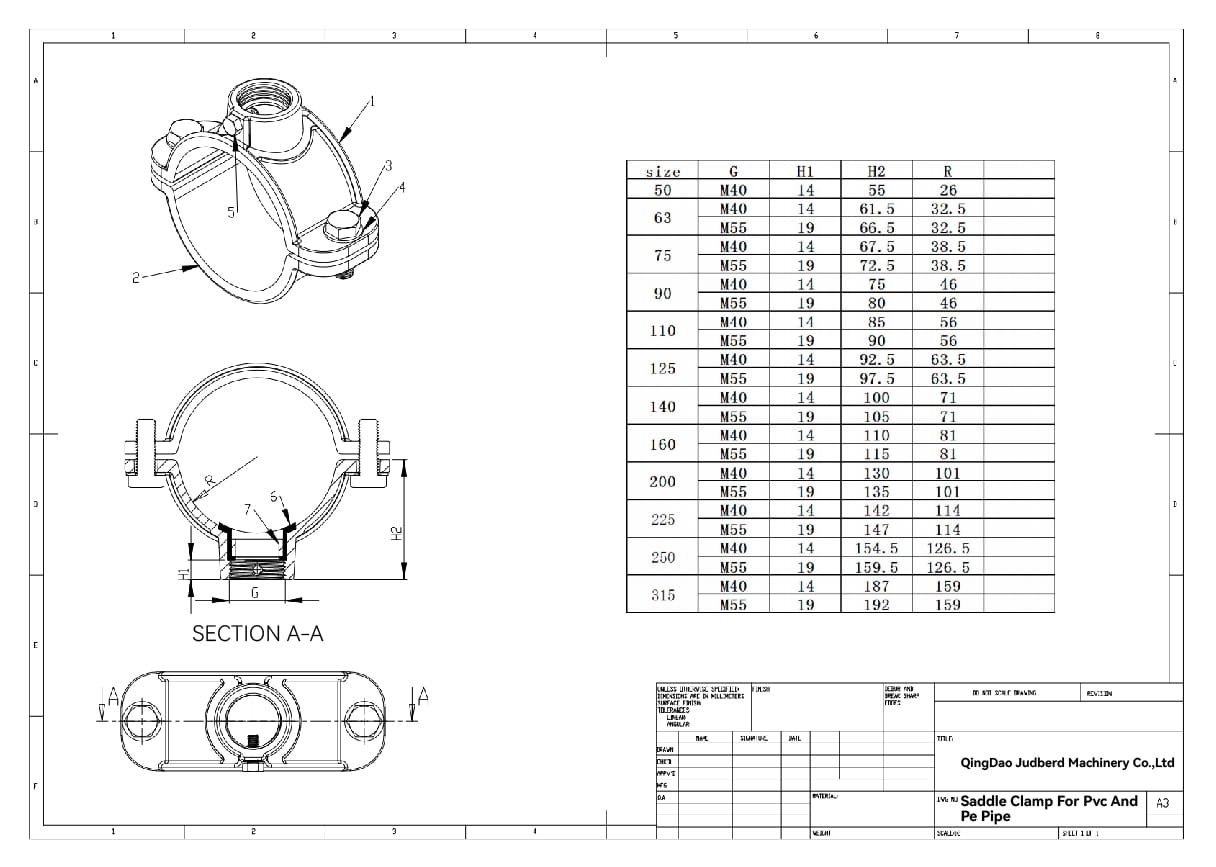
SADDLE CLAMP FOR PVC AND PE PIPE DRAWING
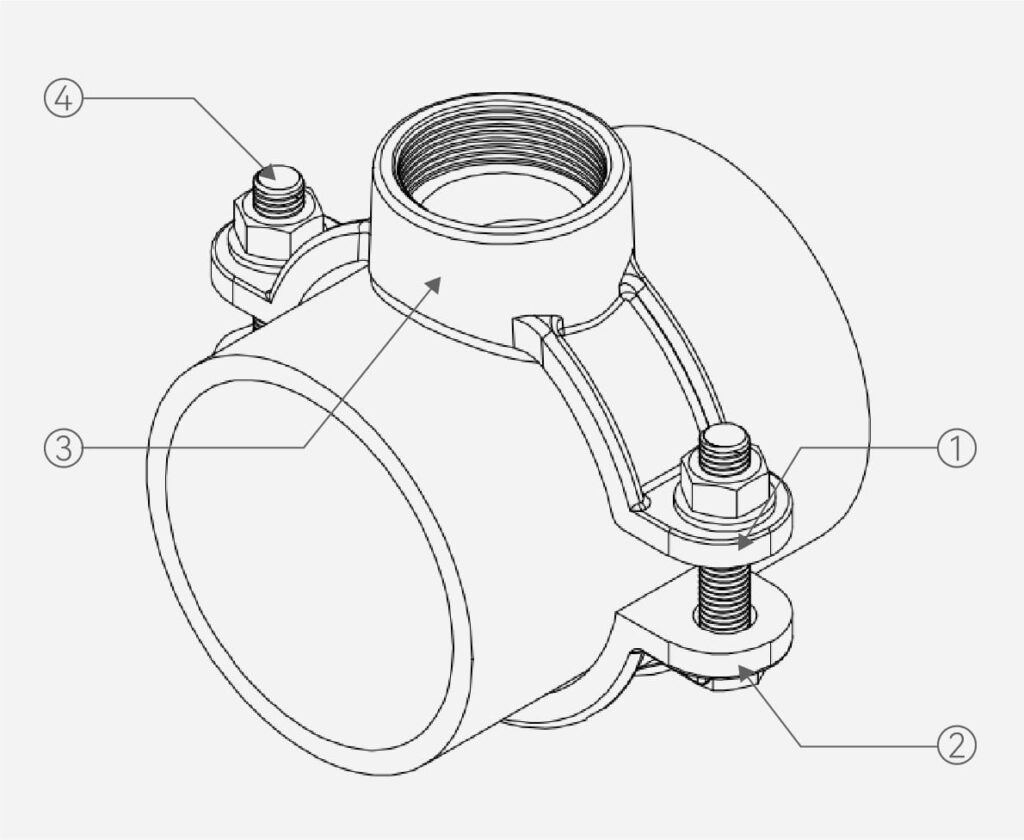
SADDLE CLAMP PARTS
A saddle clamp typically consists of two symmetric halves that are fastened together with bolts and nuts. A sealing gasket is placed between the saddle clamp and the pipe, and the gasket is compressed by tightening the bolts to create a seal and prevent leaks.
SADDLE CLAMP WORKING PRINCIPLE
A Saddle Clamp is divided into two parts that encircle the pipe.
By tightening the bolts, pressure is applied to deform the Saddle Clamp and compress the rubber gasket against the drilled hole, thus creating a seal around the hole.
SADDLE CLAMPS CATEGORIES
Saddle Clamps are categorized into different types based on their design and application:
WIDE RANGE SADDLE CLAMPS
These Saddle Clamps have a wide range and can be used on pipes which pipe OD is included in saddle clamp range, this type saddle clamp can reduce stock quantity because same saddle clamp can be used on different pipes.
PE PIPE SADDLE CLAMPS
Designed longer to accommodate the deformable nature of PE (Polyethylene) pipes.
PVC PIPE SADDLE CLAMPS
Specifically designed for use on PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes.
DI (DUCTILE IRON) PIPE SADDLE CLAMPS
Tailored for use on DI pipes.
STEEL PIPE SADDLE CLAMPS
Designed for use on steel pipes.
OTHER PIPE SADDLE CLAMPS
SADDLE CLAMPS USE
PIPELINE TAPPING
_
Used to tap into a main pipeline and divert fluid to a branch line, suitable for water supply and drainage, agricultural irrigation, and industrial pipeline systems.
EMERGENCY REPAIR
_
Can be used for quick repairs when a main pipeline is leaking to temporarily control the leak.
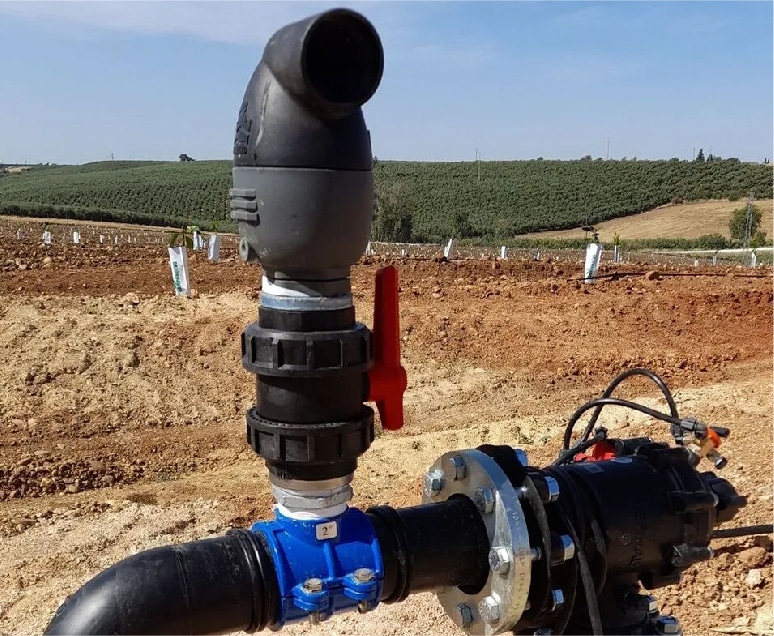
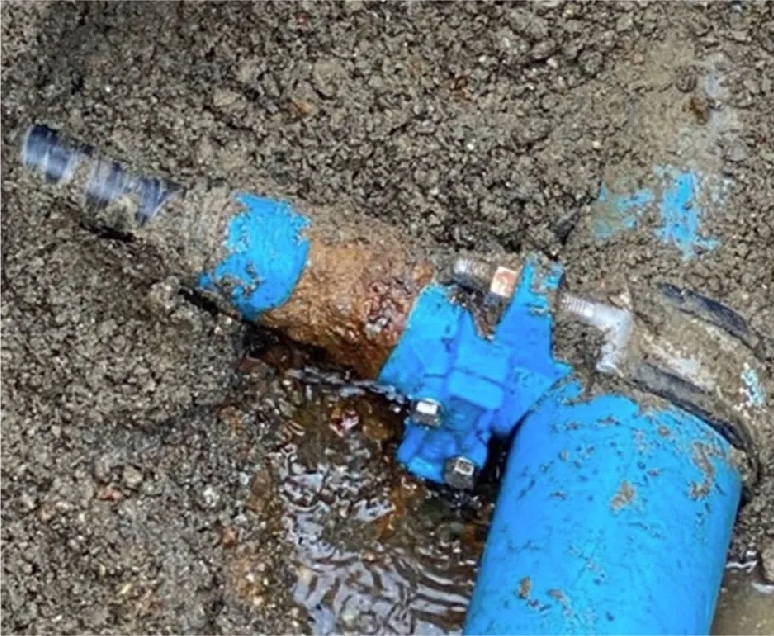



SADDLE CLAMPS INSTALLATION
When installing a saddle clamp, it can be done in two different ways:
HOT TAP (ALSO CALLED WET TAP) AND DRY TAP.
In the case of hot tap, the installation steps for a saddle clamp are as follows
Step1: Prepare tools and materials
Saddle clamp
Installation tools (such as wrenches, bolts, etc.)
Sealing gasket
Cutting tools (such as drill bits, etc.)
Step2: Identify the installation location
Determine the specific installation location on the main pipeline based on project requirements.
Ensure that the selected location is free of obvious defects and can withstand installation and operating pressures.
Step3: Clean the surface of the main pipeline
Thoroughly clean the surface of the main pipeline using cleaning tools or solvents to ensure there is no oil, rust, or other impurities.
Step4: Install the saddle clamp
Wrap the two halves of the saddle clamp around the main pipeline and place the sealing gasket between the two halves.
Fasten the two halves of the saddle clamp together with bolts, ensuring that the clamping force is evenly distributed to avoid localized stress.
Step5: Perform a sealing test
Conduct a preliminary check for leaks to ensure there are no obvious leaks between the saddle clamp and the main pipeline.
Step6: Perform the hot tap
operation
Using specialized hot tap equipment, drill a hole without stopping the normal operation of the main pipeline.
After completing the drilling, install the necessary valves and connecting pipelines to ensure the new branch line is properly connected to the main pipeline.
Step7: Inspect and
test
After installation is complete, conduct a comprehensive system check to ensure there are no leaks at any connection points.
Gradually restore the system pressure and conduct operational tests to ensure the saddle clamp is securely installed and operating correctly.
By following these steps, you can successfully install a saddle clamp while the pipeline is continuously flowing, allowing you to divert flow from the main pipeline to a branch pipeline.
In the case of dry tap, the installation steps for a saddle clamp are as follows
Step1: Prepare tools and materials
Saddle clamp
Installation tools (such as wrenches, bolts, etc.)
Sealing gasket
Cutting tools (such as drill bits, etc.)
Step2: Identify the installation location
Determine the specific installation location on the main pipeline based on project requirements.
Ensure that the selected location is free of obvious defects and can withstand installation and operating pressures.
Step3: Close the main pipeline
Shut off the fluid in the main pipeline to ensure no liquid or gas escapes during installation.
Drain any remaining fluid from the main pipeline to relieve pressure.
Step4: Clean the surface of the main pipeline
Thoroughly clean the surface of the main pipeline using cleaning tools or solvents to ensure there is no oil, rust, or other impurities.
Step5: Install the saddle clamp
Wrap the two halves of the saddle clamp around the main pipeline and place the sealing gasket between the two halves.
Fasten the two halves of the saddle clamp together with bolts, ensuring that the clamping force is evenly distributed to avoid localized stress.
Step6: Cut and drill
Use cutting tools to drill a hole in the main pipeline.
After cutting, ensure the cut is smooth and free from burrs.
Step7: Install the connecting pipelines
Install the necessary valves and connecting pipelines at the drilled hole to ensure the new branch line is properly connected to the main pipeline.
Step8: Perform a sealing test
Conduct a preliminary check for leaks to ensure there are no obvious leaks between the saddle clamp and the main pipeline.
Step9: Restore the system
Turn the fluid back on in the main pipeline, gradually restore the system pressure, and conduct operational tests to ensure the saddle clamp is securely installed and operating correctly.
By following these steps, you can successfully install a saddle clamp when there is no flow in the pipeline,
allowing you to divert flow from the main pipeline to a branch pipeline.
Saddle Clamps Types
Saddle clamps are typically categorized into the following types based on their functionality:
STANDARD SADDLE CLAMP
_
Primarily used to tap into a main pipeline and divert flow to a smaller branch line. This type is commonly used in low-pressure and medium-pressure water pipe systems.
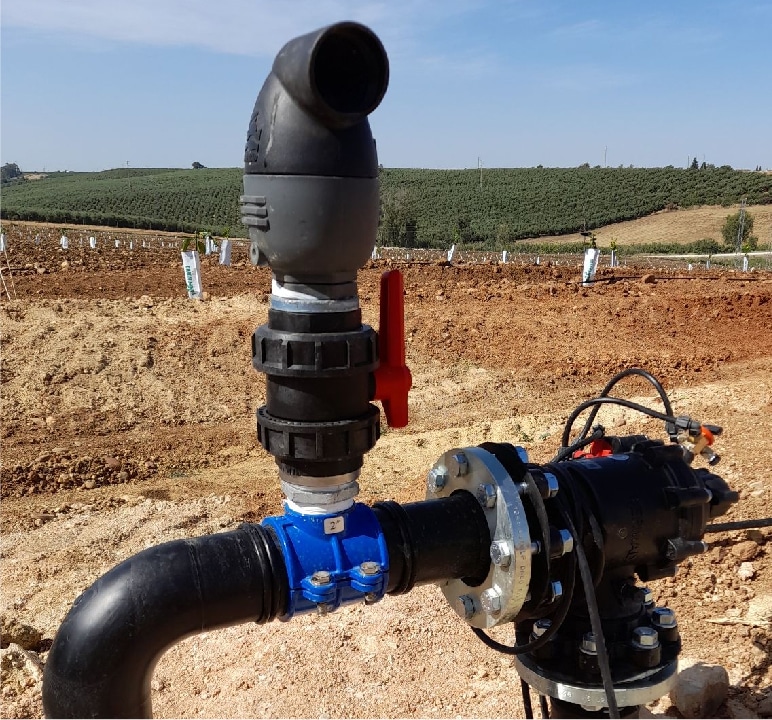

SADDLE CLAMP WITH VALVE
_
An enhancement of the standard saddle clamp that includes a valve for controlling the opening and closing of the diversion. This type is commonly used in applications where frequent operation is required.
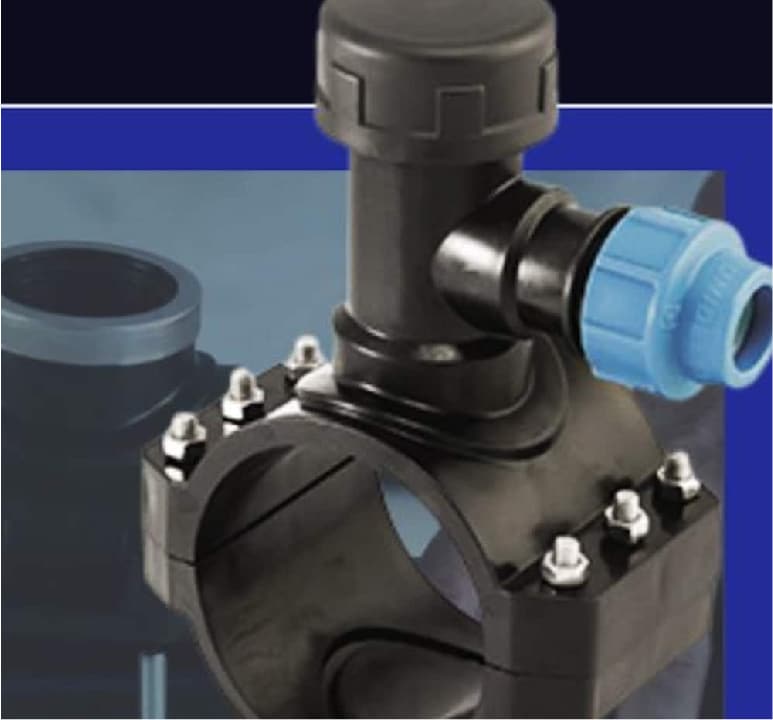

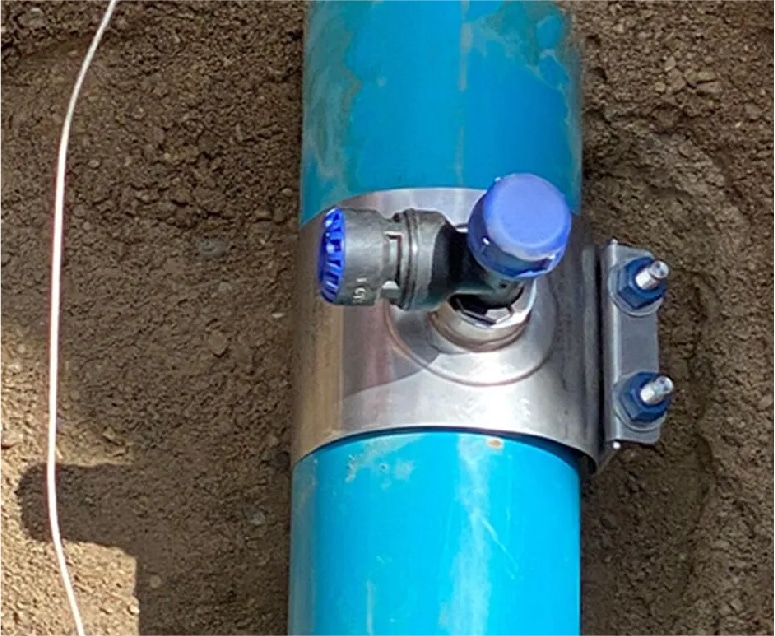
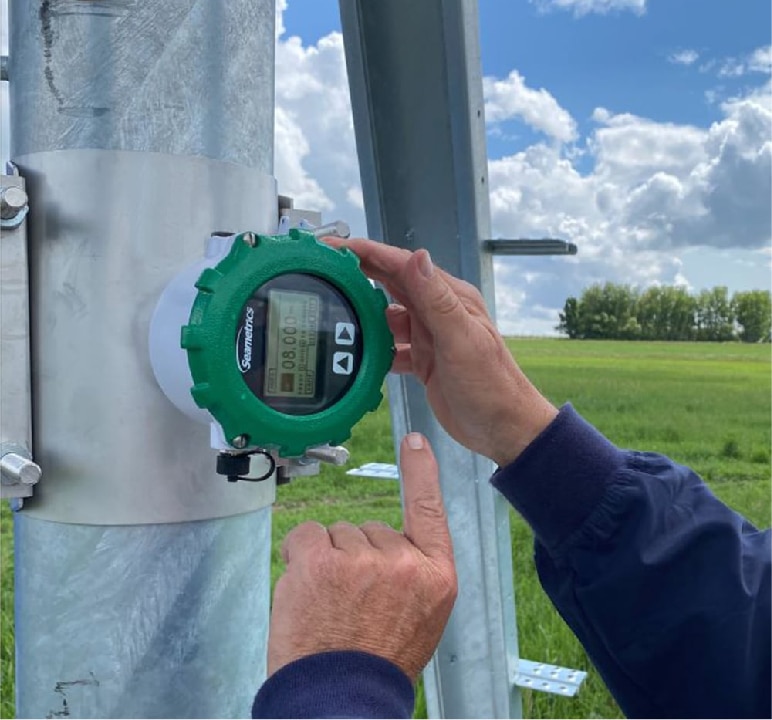
SADDLE CLAMP WITH FLOW METER
_
A saddle clamp that incorporates a flow meter for real-time monitoring of the flow in the diversion pipe. This type is used in systems where flow monitoring is required.

SADDLE CLAMP WITH CONNECTOR
_
A saddle clamp with a standard connector for quickly connecting other equipment or pipelines. This type is used in applications where quick installation and disassembly are required.
REINFORCED SADDLE CLAMP
_
Designed with additional reinforcement for use in high-pressure pipeline systems to withstand greater pressure and loads.
THESE DIFFERENT TYPES OF SADDLE CLAMPS CATER TO THE NEEDS OF VARIOUS PIPELINE SYSTEMS AND FIND WIDESPREAD USE IN A VARIETY OF APPLICATIONS.
SADDLE CLAMPS MATERIAL
The materials of various parts of the saddle clamp can vary depending on the application requirements and the environment in which they are used.
Here are some common materials:
SADDLE CLAMP BODY (TWO HALVES)
● DUCTILE IRON
Commonly used in the water supply and drainage industry, with high strength, suitable for medium and low-pressure pipelines.
● CARBON STEEL
Used for general industrial applications with high strength and durability.
● STAINLESS STEEL
Used in environments that require corrosion resistance, such as marine and chemical industries.
● ALUMINUM ALLOY
Used for lightweight applications.
● PLASTIC
Such as PE, PP , PVC etc., suitable for light-duty applications and less corrosive environments.
BOLTS AND NUTS
● CARBON STEEL
Suitable for general applications.
● STAINLESS STEEL
Used in environments that require corrosion resistance.
● GALVANIZED STEEL
Provides some corrosion resistance while being lower in cost.
SEALING GASKET
● RUBBER (EPDM, NBR, SBR, ETC.)
Common in general applications and offers good sealing performance.
● SILICONE
Used in high-temperature or chemically corrosive environments.
● FLUOROELASTOMER ( VITON )
Suitable for extreme temperature and chemically corrosive environments.
COATINGS (IF ANY)
● GALVANIZED
Used to provide additional corrosion protection.
Used to enhance corrosion resistance and for aesthetic purposes.
These materials can be selected and combined based on specific application scenarios and customer needs.
Saddle Clamps Standard
EN 545
(Thread standard is BSP,CC, Metric etc, Flange standard is ISO 7005-1/EN 1092)
AWWA C219
(Thread standard is NPT,Flange standard is ANSI/ASME B16.5/B16.47)
AS/NZ S2280
(Thread standard is BSP ,sometimes NPT also be used,Flange standard is AS 4087)
RFQ
HOW TO CHOOSE RIGHT SADDLE CLAMP?
1. Select the appropriate saddle clamp according to the material and outer diameter of the pipe. Because of the easy deformation of the PE pipe, it is necessary to choose a saddle clamp with a wider width for it, because the outer diameter of the PE and PVC pipes is the same in the same country, so The saddle clamp used for PE pipes can generally also be used for PVC pipes. For pipes with higher hardness like steel, iron, AC pipe etc., you can choose a narrower saddle clamp.
2. Select the saddle clamp according to the outlet thread type of the saddle clamp. If the outlet thread is a metric thread(M type), the thread will not be able to seal. You need to choose the following 1st design that is sealed by a gasket and supported by plastic ring. If the thread is BSP , NPT , CC and other types which is with sealing effect, then the thread can play a sealing role, but it is necessary to wrap a sealing plastic tape between the female and male threads. As below 2nd design.
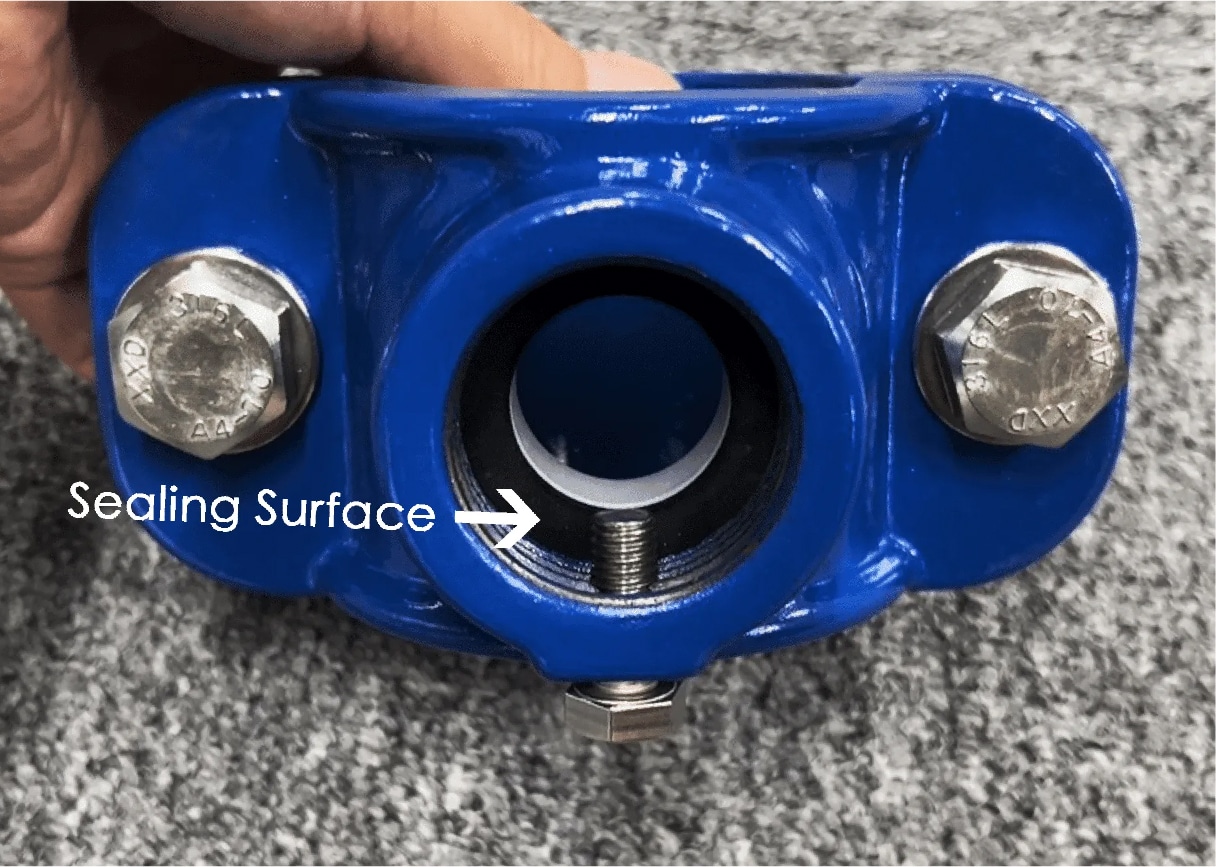

1st design
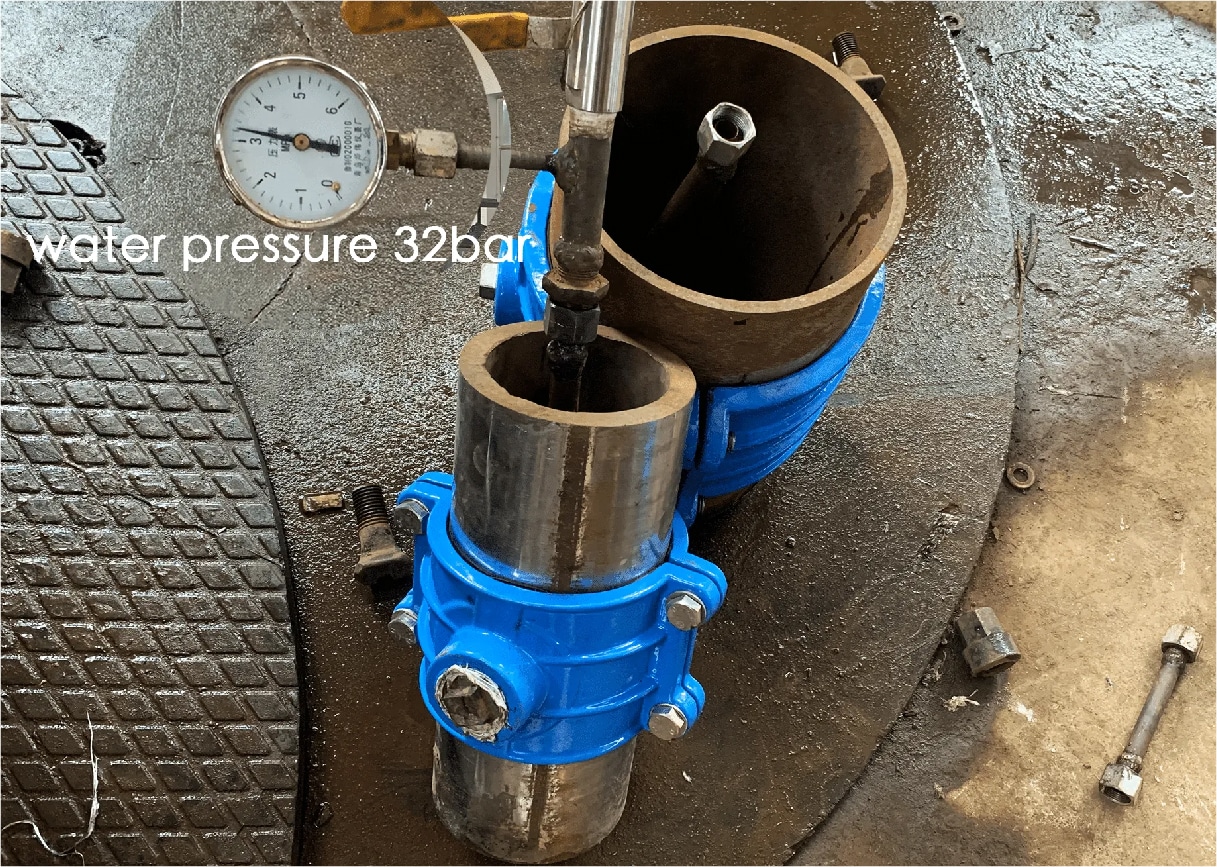

2nd design
3. If pipes of many materials are popular in the local market, in order to save inventory, you can choose a wide range saddle clamp, which can be applied to many kinds of pipes, but pay attention to comparing the outer diameter of the pipe with the design range of the saddle clamp, and ensure the pipe’s outer diameter is included in the designed range of the saddle clamp, otherwise it cannot be used.
4. For saddle clamps with steel belts, plastic pipes (PE pipes and PVC pipes) need to choose wider steel belts , while DI pipes, steel pipes, and AC pipes with higher hardness can choose narrower steel belts. Because the plastic pipe cannot bear higher pressure, it is easy to cause damage to the pipe.
STEEL BELTS DESIGN FOR DIFFERENT PIPES
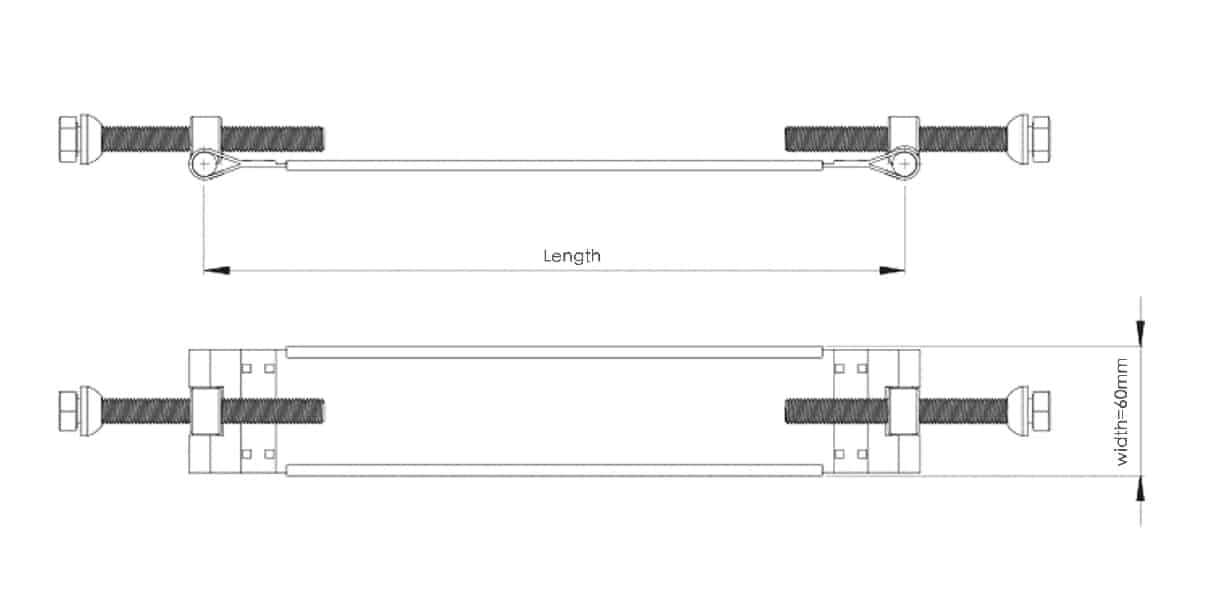
Wide belt for PE and PVC pipe
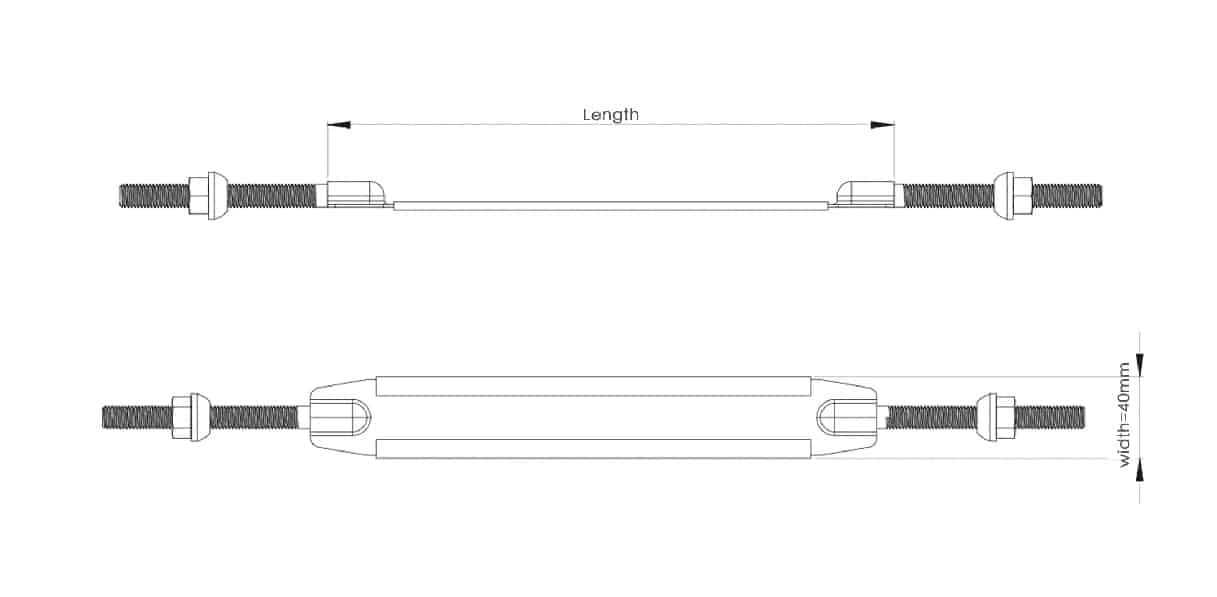
Narrow belt for DI,Steel,AC etc pipes
WHAT IS THE ADVANTAGE FOR CAST IRON SADDLE CLAMP COMPARE TO PVC PE SADDLE CLAMP?
Normally We Need To Choose Cast Iron Saddle Other Than PVC PE Saddle For Below Reason
1, Cast iron saddle clamp is much more sturdy than PE/PVC Material Saddle Clamp.
2, For saddle with threaded outlet, the threads are easily damaged and the outlet is easily cracked for PE/PVC material saddle.
3, To save the cost of frequent replacement.
4, Most of the valves connected to the saddle are made of metal such as ductile iron or copper.
5, The price is more expensive than that of PE/PVC saddle, but it is cost-effective in the long run.
6, To ensure the safety of drinking water quality.