What causes air in water pipes?
During the operation of water pipelines, Air can be generated for several reasons:
1,Air dissolved in water are released due to pressure drops or temperature increases.
2,Air present in the pipeline before water injection.
3,Air entering from the outside through gaps in pipeline connections.
How does a vacuum form in a pipe?
When water from a high-level source flows downstream by gravity at a certain speed, rapidly closing the upstream valve doesn’t immediately stop the water column in the pipeline due to the momentum of the drop and flow speed. At this moment, because air cannot enter the pipeline promptly to fill the vacuum.
The consequences of air and vacuums in pipelines
When air is present in the pipeline, it can have the following impacts
1,The presence of air increases the corrosiveness of water under its influence. Corrosion cannot occur if there is only water without air.
2,Air in the pipeline causes headloss in water flow, adding pressure load and increasing pump workload, leading to higher operational costs.
3,Air increases the risk of water hammer, potentially damaging pipeline components and creating noise.
4,The presence of air leads to inaccuracies in measuring devices like pressure gauge,flow meter etc
5,Water flow may become irregular or decrease due to the presence of air.
6,Dripping downstream after water flows into the pipeline upstream is because air pockets in the pipeline block the flow, causing water column separation.
7,Compressed air in the pipeline can rapidly expand to its limit, causing pipeline rupture.
When vacuums occurs in the pipeline
1,Negative pressure acts on the pipeline, especially in cases where the wall is thin or the pipeline is aging, leading to a shortened lifespan or, in severe cases, accidents.
2,Under negative pressure, external pollutants such as water, liquid, and soil can enter the pipeline, causing contamination.
For small-diameter ductile iron pipes, the maximum negative pressure value generally should not exceed 0.035MPa, while large-diameter thin-walled pipes can withstand a maximum negative pressure value ranging from 0.014 to 0.025MPa.
What is an air valve?
The air valve operates by using an internal float ball or float cylinder, rising or falling under the influence of air pressure and water pressure. This action controls the opening and closing of the valve’s air vent. By regulating the air vent, the valve can release or intake air, allowing the discharge of air from the pipeline or allowing external air to enter during vacuum conditions. This helps protect the pipeline, ensuring the proper functioning of the pipeline.
Judberd Air Valve
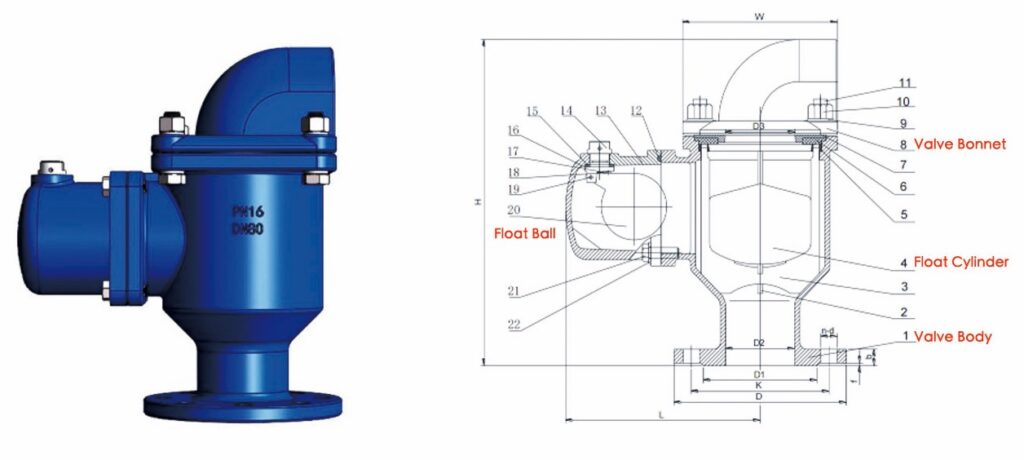
Air Valve Parts and Features
An air valve typically consists of three main parts: valve body, valve bonnet, and float ball. If used for sewage, a filter screen is added to the inlet to filter impurities in the pipeline, preventing them from affecting the movement and sealing of the float ball or float cylinder. This is especially important for air valves with float guides, as the float ball/cylinder or float guide can easily lose functionality due to debris in the sewage.
The materials for the valve body and valve cover are mainly ductile iron, stainless steel, and brass/bronze.
There are two main materials for the float ball: ABS plastic and stainless steel. The stainless steel ball actually has ABS on the inside, wrapped with stainless steel on the outside.
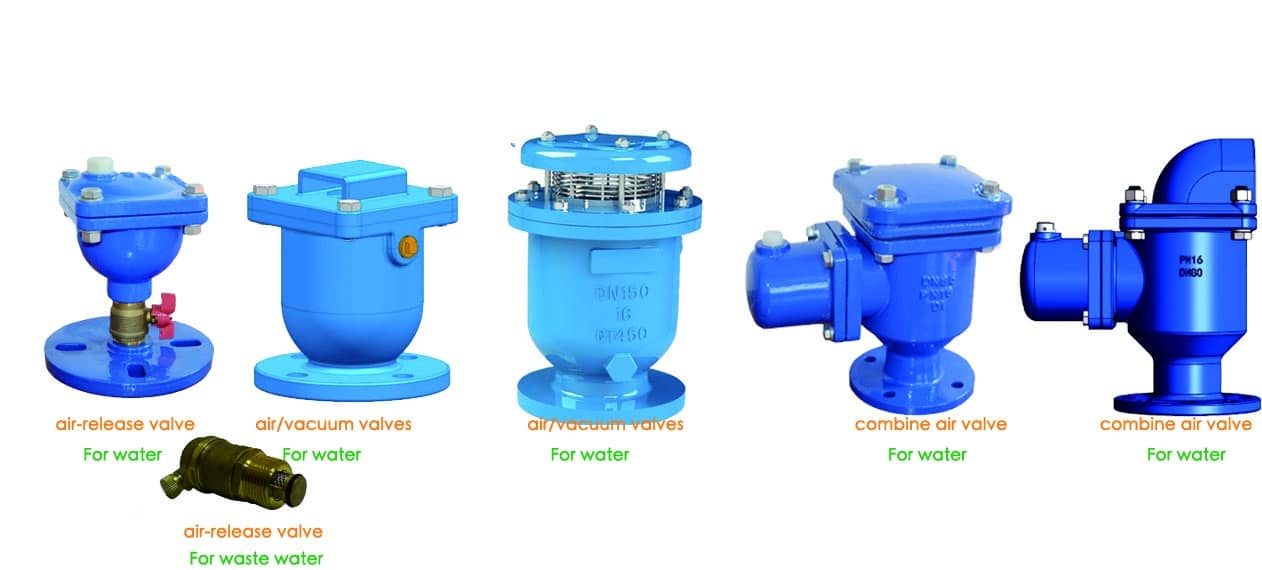
Air Valves Types
Air valves are divided into three types.
The first type is used during regular pipeline operation to automatically eliminate small amounts of air that accumulate in the pipeline due to factors such as a drop in water pressure, increase in temperature, or joint air leakage. The process is automatic; once a certain amount of air accumulates, the float ball descends to release the air. These air release valves are small in size, have threaded connections, simple structures, and flexible operation. They are commonly referred to as air-release valves.

The second type is used when the pipeline starts filling with water to release a large amount of air from the pipeline. It is also employed to allow a significant intake of air when a vacuum occurs in the pipeline. These are commonly known as air/vacuum valves. This type of air valve has a larger size and is connected with flanges.

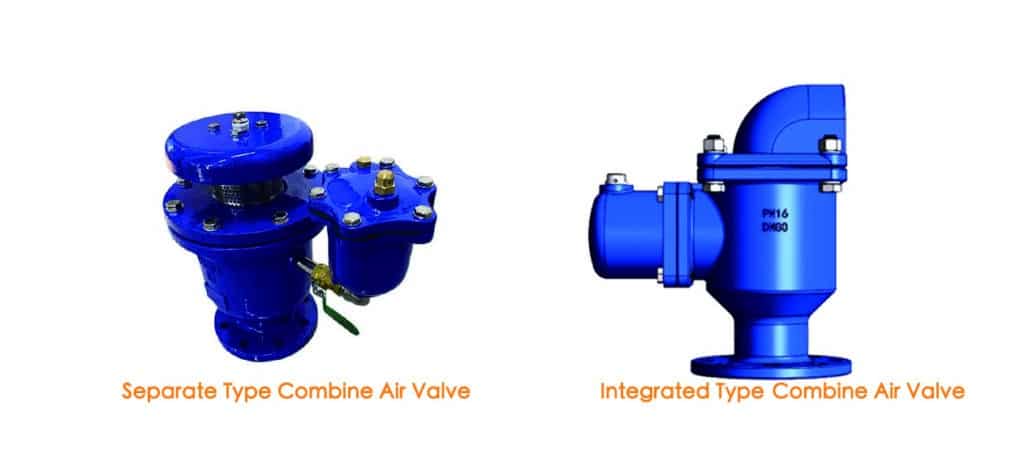
The third type is a combination of the two mentioned above, possessing the functions of both. It is the most commonly used air valve and is generally referred to as a double orifice air release valve or a combine air valve.Normally this type air valve include Integrated and separate types: The integrated type cannot be disassembled, while the separate type consists of an air/vacuum valve and an air release valve connected together. They can be detached for individual use or combined with others, as shown in the photo below.
Function of Air Valves
Air valves are crucial components in pipelines, and the correct installation of air release valves directly impacts the safety and smooth operation of the entire pipeline.
Their functions mainly include:
1 Releasing small pockets of air in the pipeline to prevent pressure loss.
2 Rapidly expelling air from the pipeline during water inflow to prevent excessive pressure that could damage the pipeline.
3 Inhaling air during pipeline drainage to prevent damage from negative pressure, which can reduce the pipeline’s lifespan or even lead to its destruction.
4 Eliminating air in the pipeline to ensure the accuracy of important measuring components like flow meters and water meters.
5 Efficiently removing air from the pipeline to prevent pump overload due to air pressure.
6 Preventing soil or external contaminants from polluting the pipeline under negative pressure.
7 Smoothly purging air to prevent water hammer caused by air.
8 Efficiently removing air to prevent vibrations and noise in the pipeline caused by the presence of air.
Installation and Maintenance
The size selection and installation position of air valves
Air valves are not directly connected axially like other pipeline parts. Instead, they serve as a branch perpendicular to the pipeline. Therefore, the size of the air valve is not equal to the size of the pipeline; it is smaller than the pipeline size, as shown in the photo below.
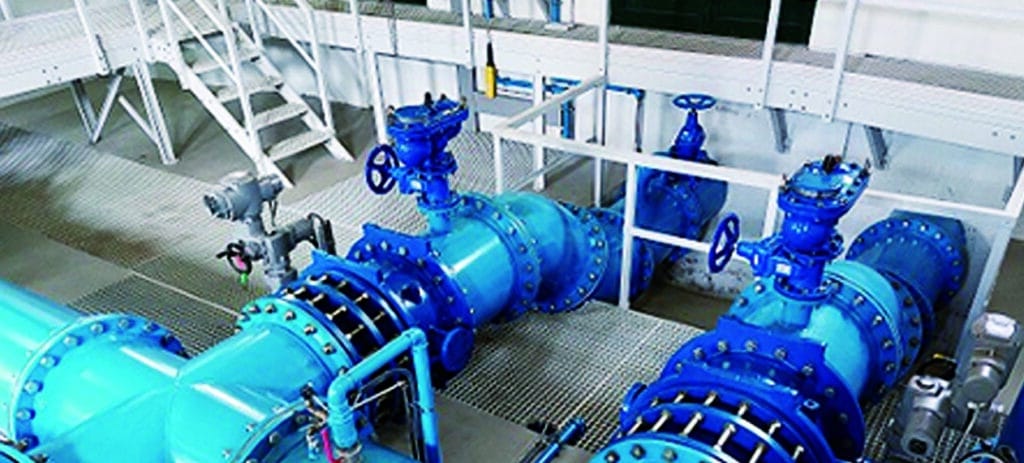

Install an air/vacuum valve between the pump and the adjacent check valve. This is necessary because, when the pump starts, the air need to be removed from the pipeline quickly. When the pump stops and the check valve closes rapidly, a vacuum can form between the check valve and the pump, requiring quick air intake. See the photo below.
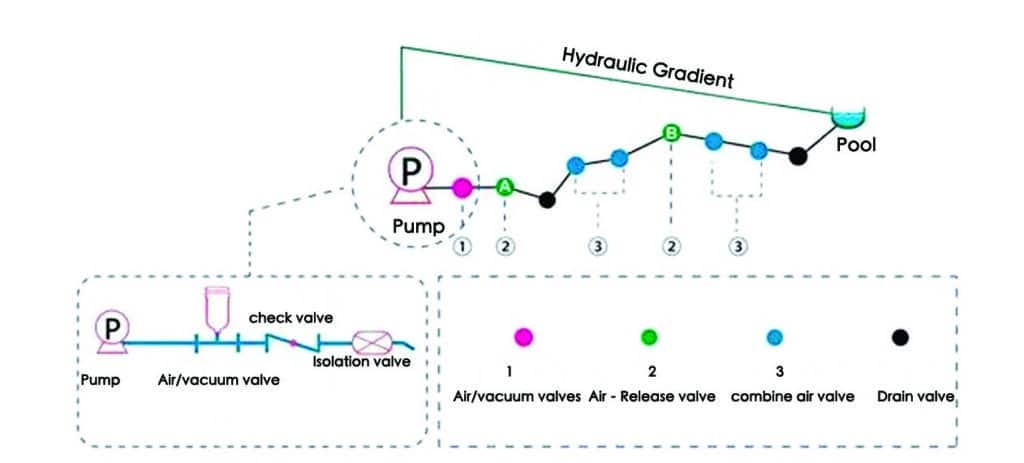
To choose the right air valve for your pipeline, refer to the AWWA Air Valve Manual.

Because the Combine air valve has both the functions of an Air-release valve and an Air/Vacuum valve, it can be used in place of either, providing more effective air release/air intake function.
Connection to Pipework
The air valve is installed as a branch at locations where air accumulates in the pipeline. The air-release valve is connected via threads, while the combine air valve and air/vacuum valve are connected via flanges. An isolation valve, which can be a gate valve, butterfly valve, ball valve, or any valve with a cutoff function, needs to be placed between the air valve and the pipeline.
Regular Inspection
Due to the importance of air valves, regular inspections are essential, requiring no less than twice a year. For wastewater with impurities, the frequency of inspections should increase based on the amount of impurities and their impact on the air valve.
Inspect whether the float ball or float cylinder of the air valve is stuck and still functioning properly. Check if any components are damaged, affecting normal operation, and ensure that the connecting bolts are tight.
Judberd is competitive manufacturer in china for air valves, if you need good quality air valves with competitive price ,contact judberd. Judberd is manufacturing vendor who not only manufacture goods for you ,we also offer professional solution for your project ….


