AWWA C515 NRS Resilient Seated Gate Valve,Threaded Ends
Threaded gate valve is a type of valve that uses a threaded connection for attachment to pipes, allowing for a secure and reliable means of controlling the flow of liquids.
Feature
● Design Standard AWWA C515
● Threaded ends standard: ANSI B1.20.1
● (Other Thread Types available upon request)
● Triple O-Rings stem seal
● Lifting lugs built into stuffing gland
● Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coating to AWWA C550 Standard
● Inspection & testing: AWWA C515
● Working Pressure: 250PSL
● Working Temperature: -20℃ To 100℃(-4°F to 212°F)
● Operator: Hand wheel , 2″Operating Nut,Gearbox

Drawing
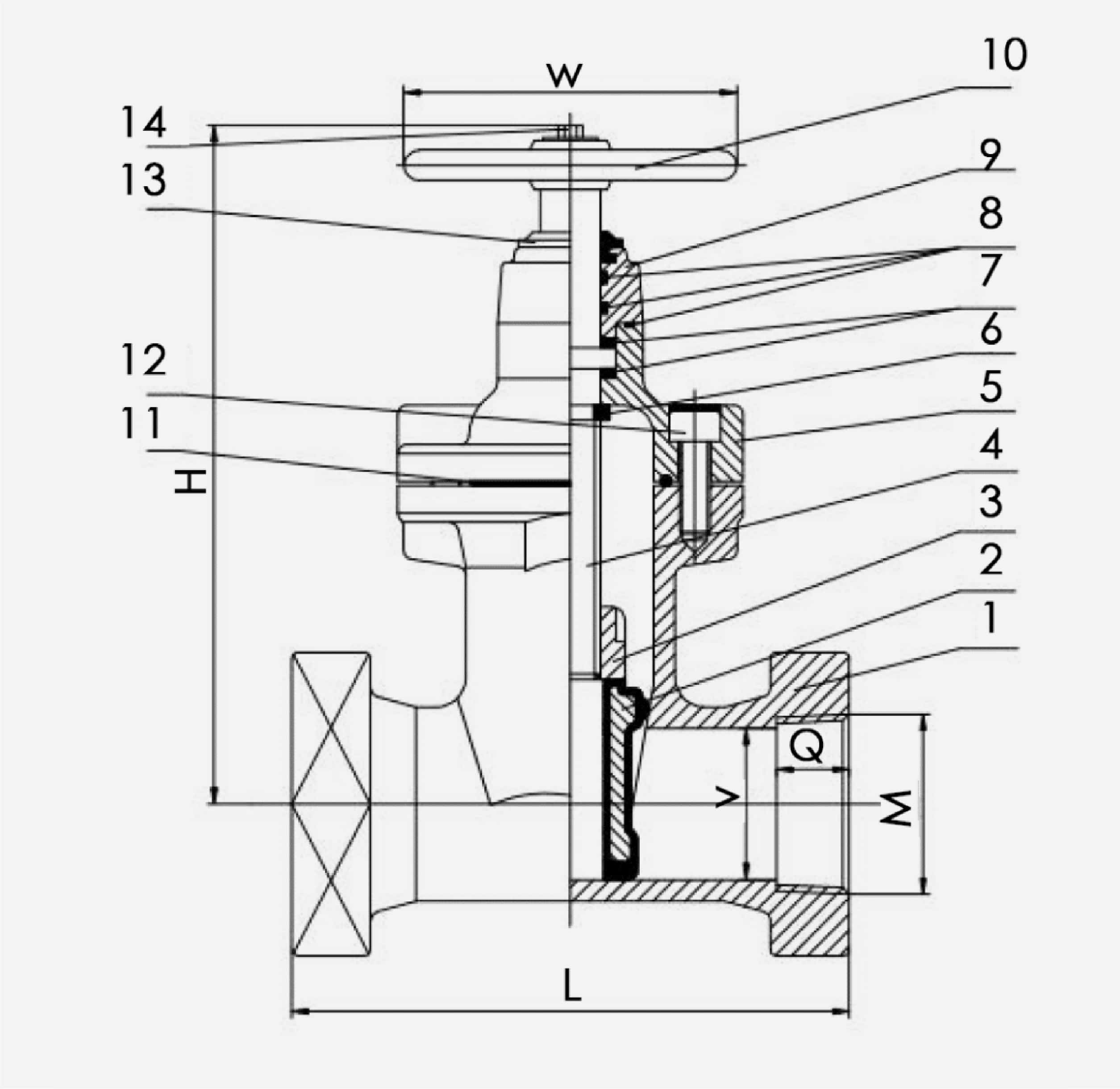
Material
1. Body
Ductile Iron ASTM A536
2. Wedge
Ductile Iron EPDM/NBR Encapsulated
3. Wedge Nut
Brass ASTM B124 C37700
4. Stem
Stainless Steel AISI 420
5. Bonnet
Ductile Iron ASTM A536
6. Wedge Nut Gasket
Rubber NBR
7. Washers
Nylon/Brass ASTM B124 C37700
8. O-ring
Rubber NBR
9. Gland
Ductile Iron ASTM A536
10. Hand wheel
Ductile Iron ASTM A536
11. Bonnet Gasket
Rubber NBR
12. Bonnet/Gland Bolt
Grand 8 Steel With ZINC Plated
13. Dust Cap
Rubber NBR
14. Hand wheel Bolts
Stainless Steel AISI304
Dimension
| Inch | L | M(NPT) | H | Q | W | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 6.5 | 1.5” | 9.05 | 0.94 | 6.3 | 1.57 |
| 2" | 7.24 | 2'' | 9.84 | 0.79 | 7.08 | 1.97 |
| 2.5" | 7.48 | 2.5'' | 10.39 | 1.14 | 7.08 | 2.56 |
| 3" | 7.99 | 3'' | 11.22 | 1.22 | 7.87 | 3.15 |
| 4" | 9.01 | 4'' | 14.17 | 1.3 | 9.84 | 3.94 |
| 6" | 10.51 | 6'' | 17.28 | 1.51 | 9.84 | 5.9 |
Feature
Threaded Connection
_
● Internal and External Threads:
The valve ends are equipped with threads (usually NPT – National Pipe Thread or BSP – British Standard Pipe) that screw into corresponding threaded pipes or fittings.
● Secure Fit:
The threaded connection ensures a tight and leak-proof fit, suitable for high-pressure applications.
Gate Valve Design
_
● Gate or Wedge:
Utilizes a gate or wedge that moves up and down to open or close the valve, controlling fluid flow. When the gate is lifted, the flow path is open; when lowered, the path is blocked.
● Body:
Typically made from durable materials such as brass, stainless steel, cast iron, or other corrosion-resistant materials.
Operation
_
● Manual or Automated:
Operated manually with a handwheel or lever, or can be equipped with actuators for automated control.
● Linear Motion:
The gate moves in a linear direction, providing a straightforward method for isolating flow.
Advantage and Disadvantage
Advantages
STRONG AND RELIABLE CONNECTION
Threaded connections provide a strong and reliable seal that can handle high pressures and temperatures.
EASY INSTALLATION
Threaded gate valves are relatively easy to install and do not require welding or specialized tools, making them suitable for various applications.
VERSATILITY
Available in a variety of sizes and materials, making them suitable for many different fluids and applications.
COST-EFFECTIVE
Generally more cost-effective than flanged or welded connections, especially in smaller pipe sizes.
Disadvantages
Potential for Leakage
_
If not properly tightened or sealed with appropriate thread sealant (like PTFE tape), threaded connections can be prone to leakage.
Difficult to Disassemble
_
Threaded joints can be difficult to disassemble, especially after long periods of use where threads may corrode or become seized.
Application
Residential and Commercial Plumbing
● Reason:
Commonly used in water supply lines, heating systems, and general plumbing applications due to their ease of installation and secure connections.
Industrial Systems
● Reason:
Suitable for industrial applications involving water, oil, gas, and other fluids where a reliable shut-off is necessary. Threaded gate valves are used in systems where frequent disassembly is not required.
Oil and Gas Industry
● Reason:
Often used in pipelines and distribution systems for oil and gas due to their ability to handle high pressures and corrosive environments.
Irrigation Systems
● Reason:
Employed in agricultural and landscape irrigation systems for controlling water flow to different zones.
Installation Steps
01
● Preparation:
Ensure that both the valve and the pipe threads are clean and free from debris. Apply a suitable thread sealant (such as PTFE tape) to the male threads of the pipe.
02
● Threading:
Screw the valve onto the threaded pipe by hand until it is hand-tight. Ensure the threads are properly engaged to avoid cross-threading.
03
● Tightening:
Use a pipe wrench or appropriate tool to further tighten the connection. Be careful not to over-tighten, as this can damage the threads or the valve body.
04
● Testing:
Once installed, turn on the fluid supply and check for leaks around the threaded connections. If leaks are detected, tighten the connection further or reapply thread sealant as needed.






